A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
SARAS PUBLICATION-MAGNETIC EFFECTS OF CURRENT AND MAGNETISM-EXAMPLE
- A current loop in a magnetic field
Text Solution
|
- A long straight wire carries a certain current and produces a magnetic...
Text Solution
|
- A circular coil ABCD carrying a current i is placed in a uniform magne...
Text Solution
|
- A bar magnet of magnetic moment M is placed at right angles to magneti...
Text Solution
|
- Copper of fixed volume V is drawn into a wire of length l. When this w...
Text Solution
|
- In a region, the potential is represented by V (x,y,z) = 6x - 8xy - 8y...
Text Solution
|
- In an ammeter 0.2% of main current passes through the galvanometer. If...
Text Solution
|
- Two identical long conducting wires AOB and COD are placed at right ...
Text Solution
|
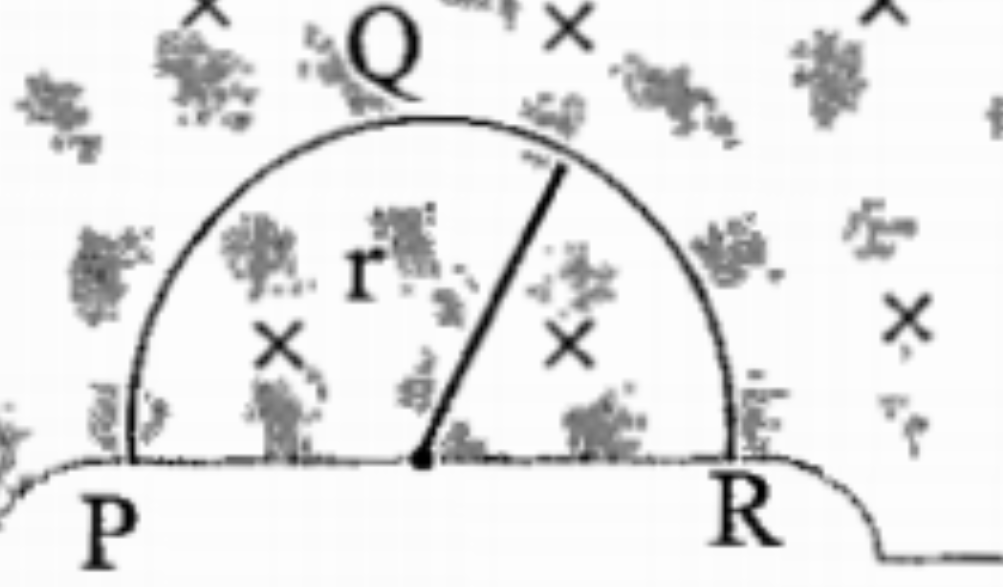
- A thin semicircular conducting ring (PQR) of radius r is falling with ...
Text Solution
|
- A wire carrying current I has the shape as shown in adjoining figure. ...
Text Solution
|
- A rectanguIar coil of length 0.12 m and width 0.1m having 50 turns of ...
Text Solution
|
- A proton and an alpha particle both enter a region of uniform magnetic...
Text Solution
|
- A long solenoid has 1000 turns. When a current of 4A flows through it...
Text Solution
|
- A long straight wire of radius carries a steady current I. The current...
Text Solution
|
- A long wire carrying a steady current is bent into a circular loop of ...
Text Solution
|
- Magnetic field induction at athe cetre O of a square loop of side a ca...
Text Solution
|
- A long solenoid of diameter 0.1 m has 2 xx 10^4 turns per meter. At th...
Text Solution
|
- In an electromagnetic wave in free space the root mean square value of...
Text Solution
|
- A 250-Turn rectangular coil length 2.1 cm and width 1.25 cm carries a ...
Text Solution
|
- An arrangement of three parallel straight wires placed perpendicular t...
Text Solution
|