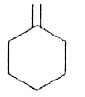
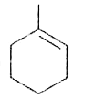
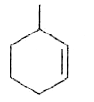
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- Aoverset("Dil. "H(2)SO(4)//Hg^(2+))to 1 - Methylcyclohexanol. Here A i...
Text Solution
|
- Anion which is protonated by dil H(2)SO(4) but produce volatile produc...
Text Solution
|
- Identify A, B and C in the following reaction CHequivCH("dil".H(2)SO(4...
Text Solution
|
- Hydrogen can be prepared by the action of dil. H(2)SO(4) on
Text Solution
|
- Why is it necessary to test for the acid radicals first with dil. H(2)...
Text Solution
|
- Which is not decomposed by dil. H(2)SO(4) ?
Text Solution
|
- But -1- yne and but -2- yne are treated with dil . H(2) SO(4) in ...
Text Solution
|
- Hydrogen can be prepared by the action of dil. H(2)SO(4) on
Text Solution
|
- Ethoxy ethane with dil. H(2)SO(4) gives
Text Solution
|