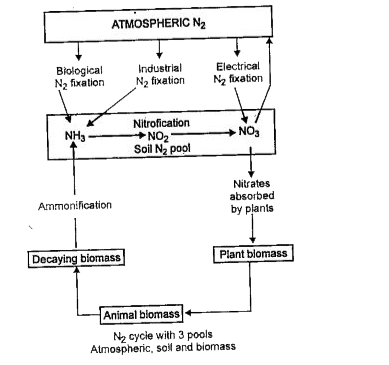
Nitrogen cycle : Source of `N_(2)`. The ultimate source of `N_(2)` is atmosphere. All `N_(2)` accumulated in biomass, detritus and humus is derived from atmosphere mainly by biological activities.
Nitrogen cycle involves activities.
I. Nitrogen fixation : It is the process of conversion of atmosphere `N_(2)` into nitrates. It further involves following methods :
1. Inductrian `N_(2)` fixation : In Harber.s process at mospheric `N_(2)` is combined with `H_(2)` to form `NH_(3)`.
`N_(2)+3H_(2) to 2NH_(3)`
2. Atmospheric nitrogen fixation : It is believed to add 35 `"mg/m"^(2)"/yr"` of `N_(2)`. In this atmospheric nitrogen combines with oxygen by takig energy from lightning to form NO, `NO_(2),HNO_(3)` which are washed by rain into soil.
3. Biological `N_(2)` fixation : Free living `N_(2)` fixing bacteria found in soil. They ar Azotobacter (Aerobic) and Clostridion (anaerobic).
Aulosira, Nostoc etc are important `N_(2)` fixing cyanobacteria. These bacteria fix 12 kg/acre/yr of at mospheric `N_(2)`.
Symbiotic `N_(2)` fixing bacteria : Rhizobium leguminosarum are found in nodules of roots o leguminous plants. they convert atmospheric `N_(2)` into nitrates. Some of the nirates are used bu them and rest of them are supplied to plants.
Frankia (actinomycetes) are found in nodules of Alnus (Non-leguminous plants) and convert atmospheric `N_(2)` into nitrates.
The nodule bacteria ca fix 50 - 100 kg of `N_(2)`/acre/yr.
I. Associative symbiotic bacterial nitrogen fixation : Azospirillum grows on surface of roots of several tropical grasses fix nitrogen. This combination where `N_(2)` fixing organisms live on the surface is known as associative symbiosis.
II. ammonification : It is the process of conversion amino acids and nitrogen present in nucleic acids contained in detritus into `NH_(3)`. It is done by actinomycetes becteria.
III. Nitrification : It is the process of converion of `NH_(3)` into nitrites and then into nitrates by nitrosomonas and nitrobacter bacteria respectively.
`4NH_(3)+7O_(2)overset("Nitrosomonas")(to)4NO_(2)+6H_(2)O`
`2NO_(2)+O_(2)overset("Nitrobactor")(to)2NO_(3)`
IV. Denitrification : It is the process of conversion of nitrates of soil into free atmospheric `N_(2)`. If the soil is waterlogged and anaerobic, then another group of microbes, the denitrifers become active Denitrifying bacteria called pseudomonas denitrificans are involved in denitrification.