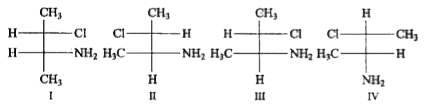
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- R, S-configuration is a useful tool for determination of enantiomers, ...
Text Solution
|
- Assign the R and S configurations to the enantiomers of 2-chlorobutane...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following structures has the R-configuration at the chir...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following structures has the S-configuration at the chira...
Text Solution
|
- In the configuration the configuration at the chiral centres are
Text Solution
|
- R,S-configuration is a useful tool for determination of enantiomers, d...
Text Solution
|
- R,S-configuration is a useful tool for determination of enantiomers, d...
Text Solution
|
- Determine the absolute configurations of the chiral centres in the fol...
Text Solution
|
- Structure of one of the enantiomer of carvone is given below. Find the...
Text Solution
|