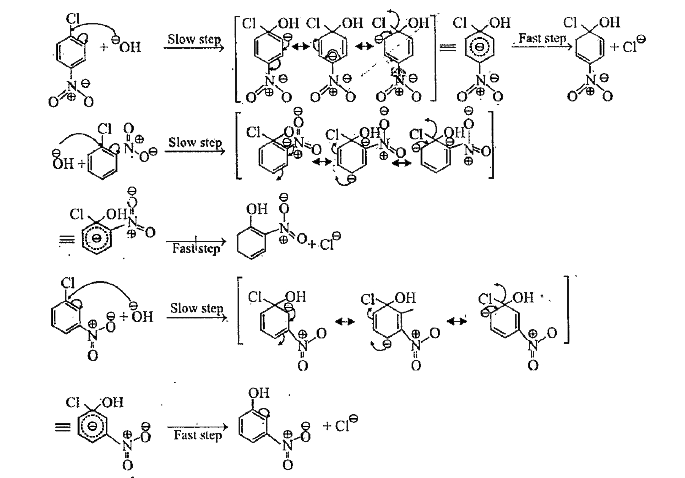
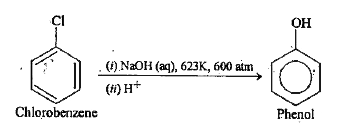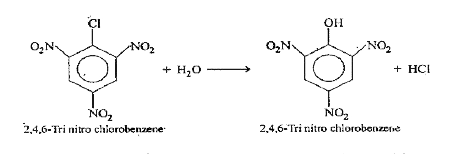Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
BETTER CHOICE PUBLICATION-HALOALKANES AND HALOARENES-QUESTIONS
- Why is Wurtz reaction not suitable for the preparation of odd number a...
Text Solution
|
- Benzyl chloride is more reactive than chlorobenzene towards nucleophil...
Text Solution
|
- Write the following reactions : Carbylamine reaction.
Text Solution
|
- Write following name reactions : Riemer Tiemann reactioin.
Text Solution
|
- Explain the following : Hoffmann amonolysis
Text Solution
|
- Write the following reactions : Williamson’s synthesis
Text Solution
|
- Explain the following reactions: Diazotisation reaction.
Text Solution
|
- Alkyl halides are amongst the most reactive of the organic compounds. ...
Text Solution
|
- Alkyl halides are regarded as synthetic tools in the hands of a chemis...
Text Solution
|
- How do the products differ when ethyl bromide reacts separately with a...
Text Solution
|
- What is the purpose of anhydrous ZnCl2 in the preparation of haloalkan...
Text Solution
|
- What happens when : Ethyl chloride is treated with (aq) KOH.
Text Solution
|
- What happens when : Methyl chloride is treated with KCN.
Text Solution
|
- Methyl bromide is treated with sodium in the presence of dry ether.
Text Solution
|
- What happens when : n-butyl chloride is treated with alcoholic KOH.
Text Solution
|
- What happens when an ethyl bromide reacts with : Ag NO2
Text Solution
|
- What happens when an ethyl bromide reacts with : Ag CN (alc.) ?
Text Solution
|
- Haloalkanes undergo nucleophilic substitution reactions while haloaren...
Text Solution
|
- How aryl halides react with sodium metal? Explain why alkyl halides sh...
Text Solution
|
- The presence of electron withdrawing group increases the reactivity of...
Text Solution
|