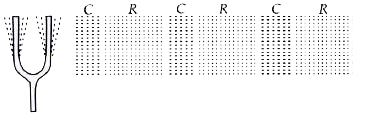Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
SOUND
MTG IIT JEE FOUNDATION|Exercise Exercise (Multiple Choice Questions) LEVEL - 1|30 VideosSOUND
MTG IIT JEE FOUNDATION|Exercise Exercise (Multiple Choice Questions) LEVEL - 2|20 VideosSOUND
MTG IIT JEE FOUNDATION|Exercise Solved Examples|15 VideosMOTION
MTG IIT JEE FOUNDATION|Exercise Olympiad/HOTS Corner|21 VideosTHRUST AND PRESSURE
MTG IIT JEE FOUNDATION|Exercise Olympiad/HOTS Corner|15 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
MTG IIT JEE FOUNDATION-SOUND-NCERT Section
- A submarine emits a sonar pulse, which returns from an underwater clif...
Text Solution
|
- What is sound and how is it produced ?
Text Solution
|
- Describe with the help of a diagram, how compressions and rarefactions...
Text Solution
|
- Cite an experiment to show that sound needs a material for its propaga...
Text Solution
|
- Why is sound wave called a longitudinal wave ?
Text Solution
|
- Which characteristic of the sound helps you to identify your friend by...
Text Solution
|
- Flash and thunder are produced simultaneously. But thunder is heard a ...
Text Solution
|
- A person has a hearing range from 20 Hz to 20 kHz. What are the typica...
Text Solution
|
- Two children are at opposite ends of an aluminium rod. One strikes the...
Text Solution
|
- The frequency of a source of sound is 100 Hz. How many times does it v...
Text Solution
|
- Does sound follow the same laws of reflection as light does ? Explain.
Text Solution
|
- When a sound is reflected from a distant object, an echo is produced. ...
Text Solution
|
- Give two practical applications of reflection of sound waves.
Text Solution
|
- A stone is dropped from the top of a tower 500 m high into a pond of w...
Text Solution
|
- A sound wave travels at a speed of 339 m//s. If its wavelength is 1.5 ...
Text Solution
|
- What is reverberation ? How can it be reduced ?
Text Solution
|
- What is loudness of sound ? What factors does it depend on ?
Text Solution
|
- Explain how bats use ultrasound to catch a prey.
Text Solution
|
- How is ultrasound used for cleaning ?
Text Solution
|
- Explain the working and application of a sonar.
Text Solution
|