Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
ACCURATE PUBLICATION-D & F BLOCK ELEMENTS -2 OR 5 MARKS QUESTIONS
- Sliver atom has completely filled d-orbitals (4d^10) in its ground sta...
Text Solution
|
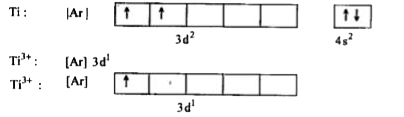
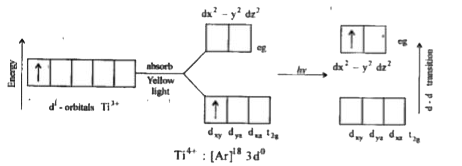
- [Ti (H2O)6]^(3+) is coloured while [Sc(H2O)6]^(3+) is colourless. Expl...
Text Solution
|
- Explain why TiCl3 is coloured but TiCl4 is colourless ?
Text Solution
|
- Explain why [Ti (H2O)6]^(3+) is violet while [Ti (H2O)6]^(4+) is colou...
Text Solution
|
- Why Cd^(2+) salts are white ? Cd=48
Text Solution
|
- Which of the two is paramagnetic V(IV) or V(V) and why ?
Text Solution
|
- Why does Mn(II) shows maximum paramagnetic character among the dival...
Text Solution
|
- Name the elements represented by following symbols : Hg , Pb , Au , Ag...
Text Solution
|
- What is atomicity ? Explain with two examples.
Text Solution
|
- What is the atomicity of the following : oxygen
Text Solution
|
- Explain why Cu(I) is diamagnetic while Cu(II) is paramagnetic in natur...
Text Solution
|
- Transition metals have high melting points and boiling points. Why?
Text Solution
|
- What is the atomicity of the following : ozone
Text Solution
|
- What is the atomicity of the following : neon
Text Solution
|
- What is the atomicity of the following : phosphorous
Text Solution
|
- What is the atomicity of the following : sulphur
Text Solution
|
- What is the atomicity of the following : sodium
Text Solution
|
- What are lanthanoids ?
Text Solution
|
- Why are Lanthanides called inner transition metals.
Text Solution
|
- What are different oxidation states exhibited by lanthanoids ?
Text Solution
|