A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
BRILLIANT PUBLICATION-STATES OF MATTER -LEVEL III (Linked Comprehension Type )
- which of the following statements is correct?
Text Solution
|
- At Boyle's temperature, compressibilitý factor Z for a real gas is:
Text Solution
|
- A very convenient method of study in PV deviation of real gases from i...
Text Solution
|
- The behaviour of a real gas. is usually depicted by plotting.compressi...
Text Solution
|
- The behaviour of a real gas. is usually depicted by plotting.compressi...
Text Solution
|
- The behaviour of a real gas. is usually depicted by plotting.compressi...
Text Solution
|
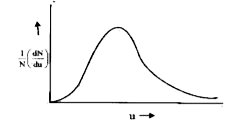
- The fraction of gaseous molecules having speed in between u and u+ du ...
Text Solution
|
- The fraction of gaseous molecules having speed in between u and u+ du ...
Text Solution
|
- The fraction of gaseous molecules having speed in between u and u+ du ...
Text Solution
|