Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
MODERN PUBLICATION-CHEMICAL KINETICS-EXERCISE
- In a pseudo first order hydrolysis of ester in water the following res...
Text Solution
|
- How can we express the rates of following reactions in terms of concen...
Text Solution
|
- How can we express the rates of following reactions in terms of concen...
Text Solution
|
- How can we express the rates of following reactions in terms of concen...
Text Solution
|
- For the reaction, N2+3H2 rarr 2NH3 the rate of reaction measured as (D...
Text Solution
|
- For the reaction : 2N2O5 rarr 4NO2+O2 the rate of reaction measured as...
Text Solution
|
- A reaction, 3X rarr 2Y+Z proceeds in a closed vessel. The rate of disa...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the reaction: 4NO2(g) + O2(g) rarr 2N2O5(g) In an experim...
Text Solution
|
- Explain with examples the meaning of the terms average rate and instan...
Text Solution
|
- A reaction 3X rarr 2Y+Z procees in a closed vessel. The rate of disapp...
Text Solution
|
- The rate of formation of a Second order dimerisation reaction is 5.8xx...
Text Solution
|
- The gas phase decomposition of COCl2, COCl2 (g) rarr CO(g) + Cl2 (g) f...
Text Solution
|
- Identify the reaction order for each of the following rate constants -...
Text Solution
|
- Identify the reaction order for each of the following rate constants -...
Text Solution
|
- Identify the reaction order for each of the following rate constants -...
Text Solution
|
- Identify the reaction order for each of the following rate constants -...
Text Solution
|
- Identify the reaction order for each of the following rate constants -...
Text Solution
|
- For a reaction: A+B rarr Products, the rate is given as k[A]^(1//3) ...
Text Solution
|
- The rate law for a reaction is found to be : Rate = k [NO2^(-) [I^(-)]...
Text Solution
|
- The rate law for a reaction is found to be : Rate = k [NO2^(-) [I^(-)...
Text Solution
|
- The rate law for a reaction is found to be : Rate = k [NO2^(-) [I^(-)...
Text Solution
|
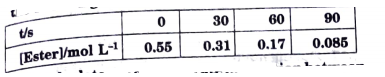 Calculate the average rate of reaction between the time interval 30 to 60 seconds.
Calculate the average rate of reaction between the time interval 30 to 60 seconds.