Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
MODERN PUBLICATION-FORCE ON A CHARGE-EXERCISE
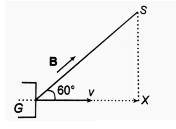
- An electron gun G emits electons of energy 2 keV travelling in the pos...
Text Solution
|
- Show that the path followed by a charged particle inside the electric ...
Text Solution
|
- Show that the path followed by a charged particles moving in a directi...
Text Solution
|
- An electron and a proton,moving parallel to each other in the same dir...
Text Solution
|
- A stream of elelctrons travelling with speed vms^-1 at right angles to...
Text Solution
|
- A hydrogen ion of mass m and charge q travels with a speed v along a c...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass m, with charge q moving with a uniform speed v, nor...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass m, with charge q moving with a uniform speed v, nor...
Text Solution
|
- Write down the expression for the Lorentz force on a charged particle.
Text Solution
|
- Write an expression for the force expereinced by a charged particle mo...
Text Solution
|
- Write a relation for the force vecF acting on a charge carrier q movin...
Text Solution
|
- Discuss the circular motion of a charged particle under the action of ...
Text Solution
|
- Deduce an expression for the frequency of revolution of a charged part...
Text Solution
|
- A charge q moving in a straight line is accelerated by a potential dif...
Text Solution
|
- A charge q moving in a straight line is accelerated by a potential dif...
Text Solution
|
- An electron beam of velocity v moving in the plane of paper enters a r...
Text Solution
|
- A particle with charge q moving with a velocity v in the plane of the ...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass m, with charge q moving with a uniform speed v, nor...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass m, with charge q moving with a uniform speed v, nor...
Text Solution
|
- Discuss the motion of charged particle in uniform magnetic field, when...
Text Solution
|
- Show that the frequency revolution of a charged pawrticle in a uniform...
Text Solution
|