Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
MODERN PUBLICATION-Radioactivity-EXERCISE
- What is beta-particle?
Text Solution
|
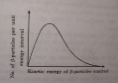
- What is beta decay? Write a brief account of beta-particl e spectrum?
Text Solution
|
- Consider the decay of the free neutron at rest: n = p + e^-. Show ...
Text Solution
|
- Explain,how radioactive nuclei can emitbeta- particles even though nuc...
Text Solution
|
- Define gamma (gamma) decay.
Text Solution
|
- What is alpha decay, beta decay and gamma decay?
Text Solution
|
- Explain radio-carbon dating.
Text Solution
|
- What is natural radioactivity ? What type of radiations are emitted ? ...
Text Solution
|
- State the law of radioactive decay. Show that radioactive decay is exp...
Text Solution
|
- State the law of radioactive decay, If N0 is the number of radioactive...
Text Solution
|
- State the law of radioactive decay, If N0 is the number of radioactive...
Text Solution
|
- Give the relation between half life and disintegration constant of a r...
Text Solution
|
- What is meant by half life of a radioactive substance? Derive expressi...
Text Solution
|
- A radioactive nucleus is represneted by the symbolbX^a,How is the new ...
Text Solution
|
- A radioactive nucleus is represneted by the symbolbX^a,How is the new ...
Text Solution
|
- A radioactive nucleus is represneted by the symbolbX^a,How is the new ...
Text Solution
|
- What is meant by half life of a radioactive substance? Derive expressi...
Text Solution
|
- Define alpha- decay and show that kinetic energy of an alpha-particle ...
Text Solution
|
- Tha half-life of U^(238) against alpha decays is 1.42 xx 10^(17)s.How ...
Text Solution
|
- Tha half-life of U^(238) against alpha decays is 1.42 xx 10^(17)s.How ...
Text Solution
|