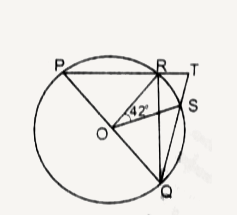
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
CIRCLE AND ITS TANGENT LINES
LUCENT PUBLICATION|Exercise EXERCISE 8B|27 VideosCIRCLE AND ITS TANGENT LINES
LUCENT PUBLICATION|Exercise EXERCISE 8B|27 VideosCENTRE OF TRIANGLE
LUCENT PUBLICATION|Exercise EXERCISE-6B|8 VideosCONGRUENCE AND SIMILAR TRIANGLES
LUCENT PUBLICATION|Exercise EXERCISE-5B|8 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
LUCENT PUBLICATION-CIRCLE AND ITS TANGENT LINES-EXERCISE 8A
- Let PAB be a secant to a circle intersecting at points A and B, and PC...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure below, if angle BAD = 60^(@), angle ADC = 105^(@), then ...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure given above, PQ is a diameter of the circle whose centre...
Text Solution
|
- In the given figure O is the centre of the circle AC and BD intersects...
Text Solution
|
- Let A and B be two points. What is the locus of the point P such that ...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure given above, O is the centre of the circle OA = 3 cm, AC...
Text Solution
|
- Two circles touch each other internally. Their radii are respectively ...
Text Solution
|
- The distance between the centres of two circles is 10 cm whose radius ...
Text Solution
|
- If the radii of two circles be 6 cm and 3 cm and the length of the tra...
Text Solution
|
- ABC is an equilateral triangle inscribed in a circle with AB = 5 cm. L...
Text Solution
|
- Two circles touch each other externally at P. Two secants APB and CPD ...
Text Solution
|
- A point P moves such that its distances from two given points A and B...
Text Solution
|
- ABCD is a cyclic quadrilateral and A + B = 2 ( C + D). If angle C gt 3...
Text Solution
|
- If diameters of two circles are 6 units and 10 units and their centres...
Text Solution
|
- Point A is situated at a distance of 6.5 cm from the centre of a circl...
Text Solution
|
- A circle with centre O is given and C is a point on its minor arc AB. ...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure, ABC is a triangle in which AB = AC. A circle through B ...
Text Solution
|
- In the given figure if angle PAQ = 59^(@), angle APD = 40^(@), then wh...
Text Solution
|
- In the adjacent figure C and D are two points on circumference of a se...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure given below, if angle AOP = 75^(@) and angle AOB = 120^(...
Text Solution
|