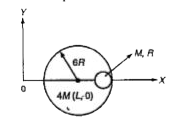
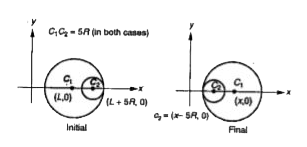
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A small sphere of radius R is held against the inner surface of a larg...
Text Solution
|
- A small sphere of radius R is held against the inner surface of a larg...
Text Solution
|
- A small sphere of radius R is held against the inner surface of larger...
Text Solution
|
- A large insulated sphere of radius r charged with Q units of electrici...
Text Solution
|
- A small body of mass 'm' is placed at the top of a smooth sphere of ra...
Text Solution
|
- A small sphere of radius R is held against the inner surface of alpha ...
Text Solution
|
- Consider eight small spheres , radius = r(s) arranged at the corner of...
Text Solution
|
- A small sphere of radius R is kept attached to the smooth inner wall o...
Text Solution
|
- ஒரு உலோகக்கோளம் உருக்கப்பட்டு சிறிய கோளங்களை செய்யப்படுகிறது. ஒவ்வொர...
Text Solution
|