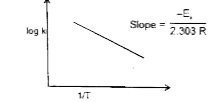
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- The activation energy E(a) of a reaction can be calculated by plottin...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion (A) : k=Ae^(-E(a)//RT) , the Arrhenius equation represents t...
Text Solution
|
- The temperature dependence of rate constant (k) of a chemical reaction...
Text Solution
|
- The activation energy for a simple chemical reaction A rarr B is E(a) ...
Text Solution
|
- In the given graph the activation energy , E(a) for the reverse reacti...
Text Solution
|
- The temperature dependence of rate constant(k) of a chemical reaction ...
Text Solution
|
- If activation energy, E(a) of the reaction is equal to RT then
Text Solution
|
- The rate constant of a first order reaction can be determined by the e...
Text Solution
|
- एक साधारण रासायनिक अभिक्रिया Ato B को अग्रिम अभिक्रिया की सक्रियण ऊर्ज...
Text Solution
|