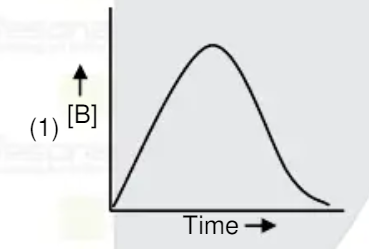
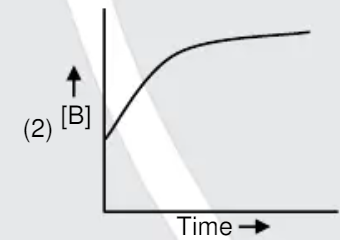
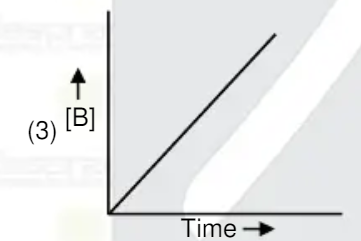
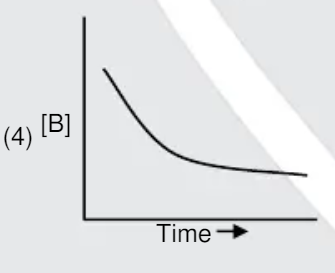
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- In a Radioactive decay A overset(k1)toB overset(k2)toC (K1gtK2) Ini...
Text Solution
|
- In a reversible reaction Aunderset(K2)overset(K1)hArrB the initial con...
Text Solution
|
- For the consecutive reaction Aoverset(k1("time"^(-1)))toBoverset(k2("t...
Text Solution
|
- A reaction is represented by A overset(k1)rarr B (slow ) and A+B overs...
Text Solution
|
- C2H5Broverset(AgCN)toAoverset(H3overseto+O)toB+HCOOH Bunderset"KOH"ove...
Text Solution
|
- If A overset(K1) hArr B,B overset(K2)hArr C,C overset(K3) D What is th...
Text Solution
|
- अभिक्रिया योजना A overset(k1)toB overset(k2)toC के लिए यदि B के बन...
Text Solution
|
- अभिक्रिया का अंतिम उत्पाद है एथिल एमीन overset(HNO2)toA overset(PCl...
Text Solution
|
- In order of reaction A overset(K1)to B overset(K2)to C overset(K3)toD,...
Text Solution
|