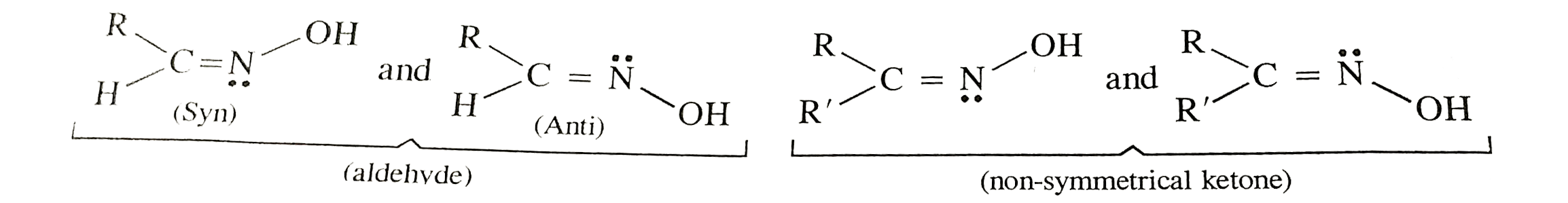
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- The reactions of hydroxylamine with a symmetrical ketone (R(2)C = O) f...
Text Solution
|
- Explain Nucleophilic addition reaction mechanism of aldehydes and keto...
Text Solution
|
- Aldehydes and ketones , on treatment with hydroxylamine give
Text Solution
|
- Assertion: Oximes are less acidic than hydroxyl amine. Reason: Oxim...
Text Solution
|
- Nucleophilic addition reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones- Part 1
Text Solution
|
- Nucleophilic addition reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones- Part 2
Text Solution
|
- Explain the mechanism of nucleophilic addition reactions of aldehyde a...
Text Solution
|
- The characteristic reactions of aldehydes & ketones is
Text Solution
|
- प्रक्कथन : हाइड्रॉक्सिल एमीन की अपेक्षा ऑक्सिम कम अम्लीय होते हैं। क...
Text Solution
|