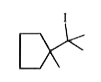
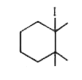
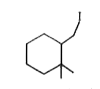
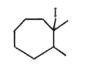
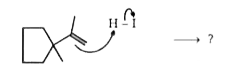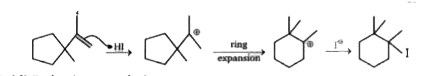A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
MS CHOUHAN-HYDROCARBONS (ALKENES)-LEVEL-2
- Taking into account the stability of various cycloalkanes and carbocat...
Text Solution
|
- In each reagent box write a letter designating the best reagent and co...
Text Solution
|
- Propene (CH3 – CH = CH2) can be transformed to compounds (a to j) list...
Text Solution
|
- In each reaction box write a single letter designating the best reagen...
Text Solution
|
- Match the reagents a-j with products A-J. There is one best product fo...
Text Solution
|
- Match the column :
Text Solution
|
- Match the column I with column II and with column III (Matrix).
Text Solution
|
- Match the column I and II.
Text Solution
|
- Sum of molecular mass of A, B, C, D (i.e. A+B + C + D) is equal to :
Text Solution
|
- underset("(all isomers) ")(C2FClBrl) underset(Ni) overset(H2)to (A)(ex...
Text Solution
|
- How many products are formed by sum of P,Q,R,S ?
Text Solution
|
- Vladimir Markovnikov rule : Alkenes undergo electrophilic addition rea...
Text Solution
|
- Vladimir Markovnikov rule : Alkenes undergo electrophilic addition rea...
Text Solution
|
- Vladimir Markovnikov rule : Alkenes undergo electrophilic addition rea...
Text Solution
|
- Vladimir Markovnikov rule : Alkenes undergo electrophilic addition rea...
Text Solution
|
- Vladimir Markovnikov rule : Alkenes undergo electrophilic addition rea...
Text Solution
|
- Vladimir Markovnikov rule : Alkenes undergo electrophilic addition rea...
Text Solution
|
- CH3 - CH2-CH=CH2+CH2 OH overset(H^(o+))to CH3-CH2- underset(OCH3) un...
Text Solution
|
- CH3 - CH2-CH=CH2+CH2 OH overset(H^(o+))to CH3-CH2- underset(OCH3) un...
Text Solution
|
- CH3 - CH2-CH=CH2+CH2 OH overset(H^(o+))to CH3-CH2- underset(OCH3) un...
Text Solution
|
- CH3 - CH2-CH=CH2+CH2 OH overset(H^(o+))to CH3-CH2- underset(OCH3) un...
Text Solution
|