Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
NEWTON'S LAWS OF MOTION
HC VERMA|Exercise Questions for short Answer|17 VideosNEWTON'S LAWS OF MOTION
HC VERMA|Exercise Objective -1|14 VideosNEWTON'S LAWS OF MOTION
HC VERMA|Exercise Exercises|42 VideosLAWS OF THERMODYNAMICS
HC VERMA|Exercise Short Answer|14 VideosPHYSICS AND MATHEMATICS
HC VERMA|Exercise Exercises|34 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
HC VERMA-NEWTON'S LAWS OF MOTION-worked out Examples
- A body of mass m is suspended by two strings making angles alpha and ...
Text Solution
|
- Two bodies of masses m1 and m2 are connected by a light string going ...
Text Solution
|
- A bullet moving at 250 m/s penetrates 5 cm into at tree limb before co...
Text Solution
|
- The force on a particle of mass 10 g is (veci10 + vecj5)N. If it start...
Text Solution
|
- Match the following :
Text Solution
|
- A block A of mass m is tied to a fixed point C on a horizontal table t...
Text Solution
|
- A smooth ring A of mass m can slide on a fixed horizontal rod. A strin...
Text Solution
|
- A light rope fixed at one end of a wooden clamp on the ground passes o...
Text Solution
|
- Three blocks of masses m1, m2 and m3 are connected as shown in the fig...
Text Solution
|
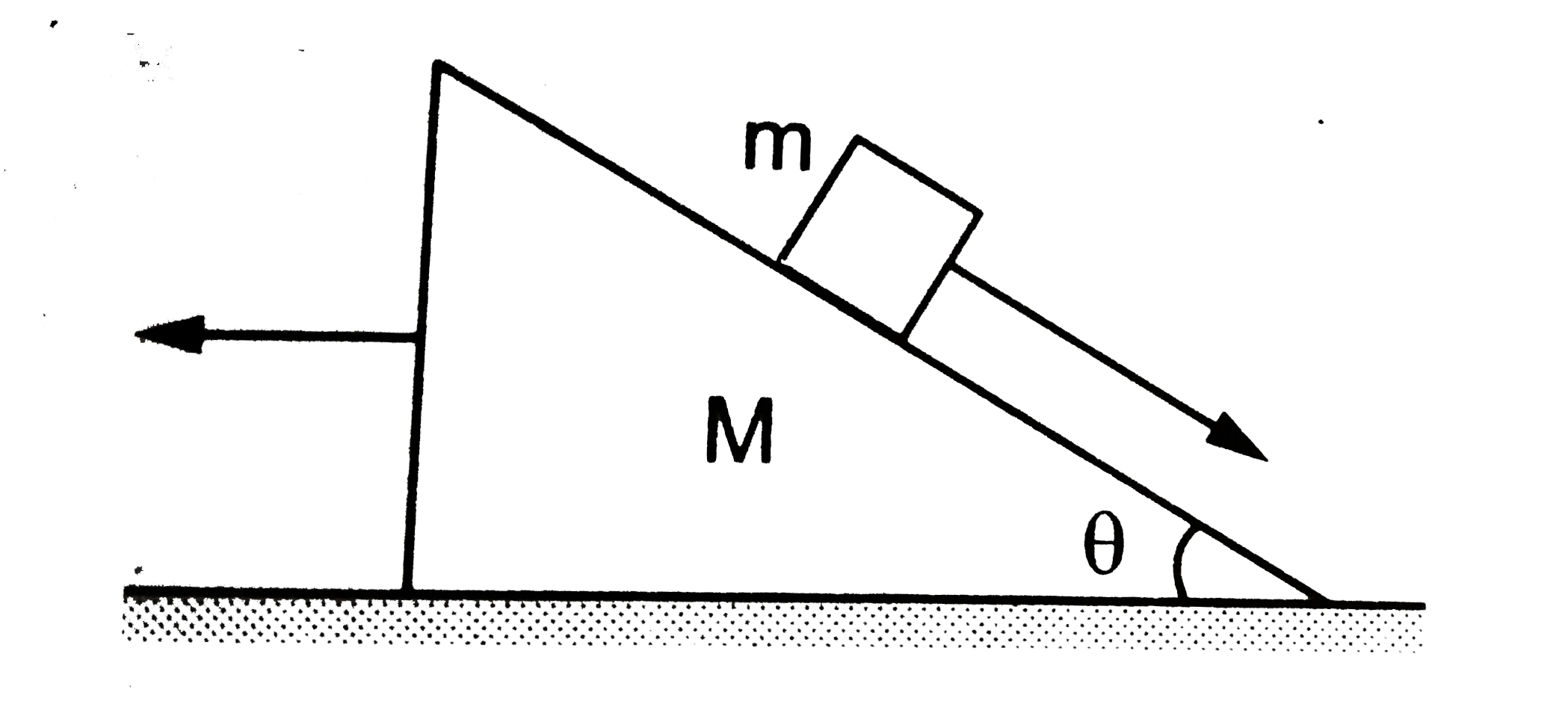
- A particle slides down a smooth inclined plane of elevation theta fixe...
Text Solution
|
- All the surfaces shown in figure are assumed to be frictionless. The b...
Text Solution
|