Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
HC VERMA-WORK AND ENERGY-Exercises
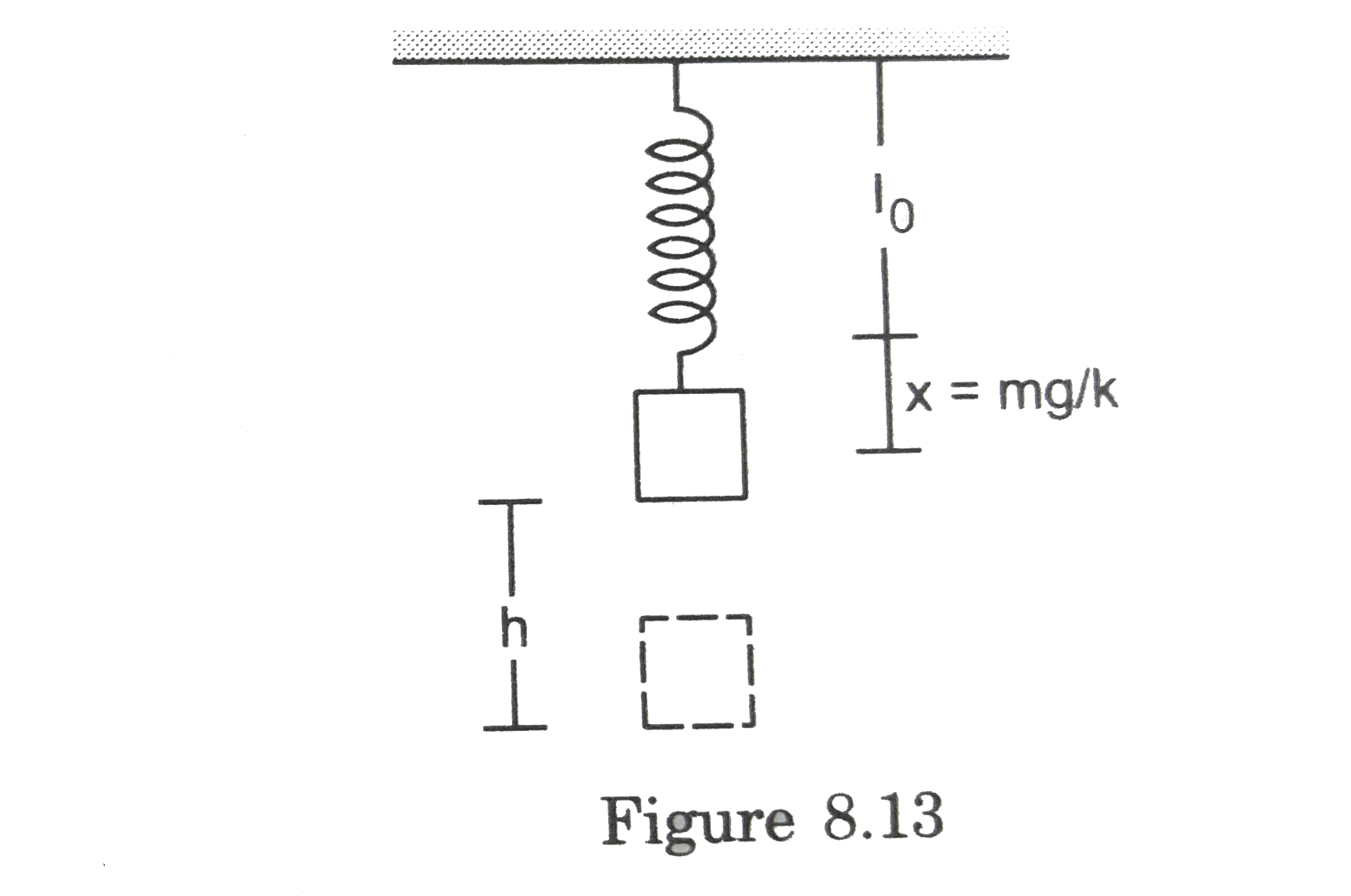
- A block of mass m is suspended through a spring of spring constant k a...
Text Solution
|
- The mass of a cyclist together with the bicycle is 90 kg. Calculate th...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass 2.00 kg moving at a speed of 10.0 m/s accelerates at 3...
Text Solution
|
- A box is pushed through a distance of 4m across a floor offering 100N ...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass 5.0 kg slides down an incline of inclination 30^0 and ...
Text Solution
|
- A constant force of 2.50 N accelerates a stationary particle of mass 1...
Text Solution
|
- The amount of work done by centripetal force on the object moving in a...
Text Solution
|
- A man moves on a straight horizontal road with a block of mass 2 kg i...
Text Solution
|
- A force F=a+bx acts on a particle in the x-directioin, where a and b a...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass 250 g slides down an incline of inclination 37^0 with ...
Text Solution
|
- In the adjacent figure BE bot DA and CDbotDA then prove that mangle1 ~...
Text Solution
|
- A box weighing 2000 N is to be slowly slid through 20 m on a straigh t...
Text Solution
|
- A block of weight 100 N is slowly slide up on a smooth incline of incl...
Text Solution
|
- Find the average frictional force needed to stop a a car weighing 500 ...
Text Solution
|
- Find the averasge force needed to accelerate a car weighing 500 kg for...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass m moves on a straight line with its velocity varyin...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass 2.0 kg kept at rest on an inclined plane of inclinatio...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass 2.0 kg is pushed down an inclined plane of inclination...
Text Solution
|
- A 250 g block slides on aeroug horizontal table. Find the work donen b...
Text Solution
|
- Water falling from a 50 m high fall is to be used for generating elect...
Text Solution
|
- A person is climbing a ladder with a suitcase on his head. Then the wo...
Text Solution
|