Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
HC VERMA-ROTATIONAL MECHANICS-Exercises
- A light rod of length 1 m is pivoted at its centre and two masses of 5...
Text Solution
|
- Suppose the rod in the previous problem has a mass of 1 kg distributed...
Text Solution
|
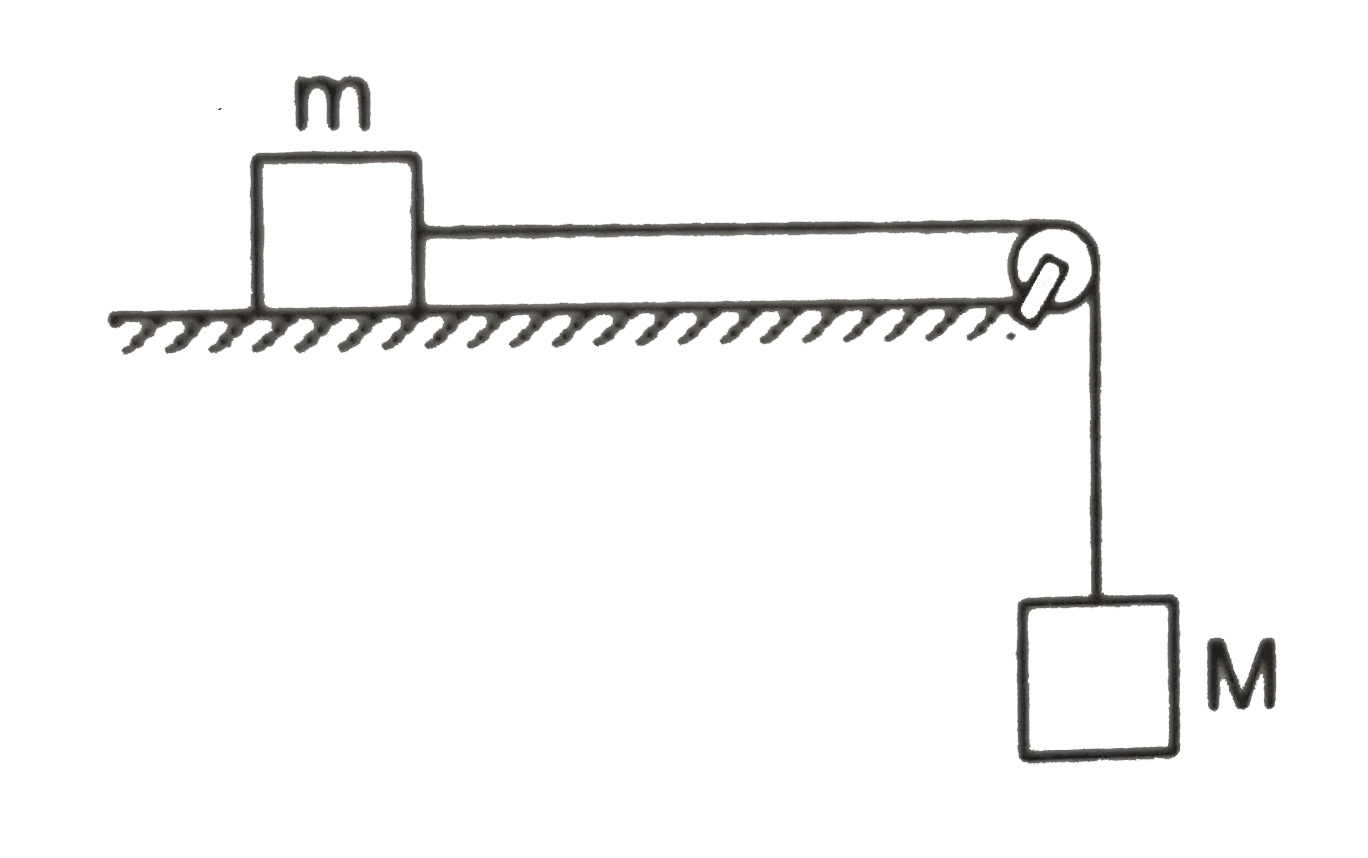
- Figure shows two blocks of masses m and M connected by a string passin...
Text Solution
|
- A string is wrapped on a wheel of moment of inertia 0.20 kg-m^2 and ra...
Text Solution
|
- Suppose the smaller pulley of the previous problem has its radius 5.0 ...
Text Solution
|
- The pulleys in figure are identical, each having a radius R and moment...
Text Solution
|
- The descending pulley shown in figure has a radius 20 cm and moment of...
Text Solution
|
- The pulley shown in figure has a radius 10 cm and moment of inertia 0....
Text Solution
|
- Solve the previous problem if the firction coefficient between the 2.0...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform metre stick of mass 200 g is suspended from the ceiling thro...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform ladder of length 10.0 m and mass 16.0 kg is resting against ...
Text Solution
|
- Suppose the friction coefficient between the ground and the ladder of ...
Text Solution
|
- A 6.5 m long ladder rests against as vertical wall reaching a height o...
Text Solution
|
- the door of an almirah is 6 ft high, 1.5 ft wide and weights 8 kg. The...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform rod of length L rests against a smooth roller as shown in fi...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform rod of mass 300 g and length 50 cm rotates at a uniform angu...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform square plate of mass 2.0 kg and edge 10 cm rotates about one...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the ratio of the angular momentum of the earth about its axi...
Text Solution
|
- Two particles of masses m1 and m2 are joined by a light rigid rod of l...
Text Solution
|
- A dumb bell consists of two identicasl small balls offmss 1/2 kg each ...
Text Solution
|