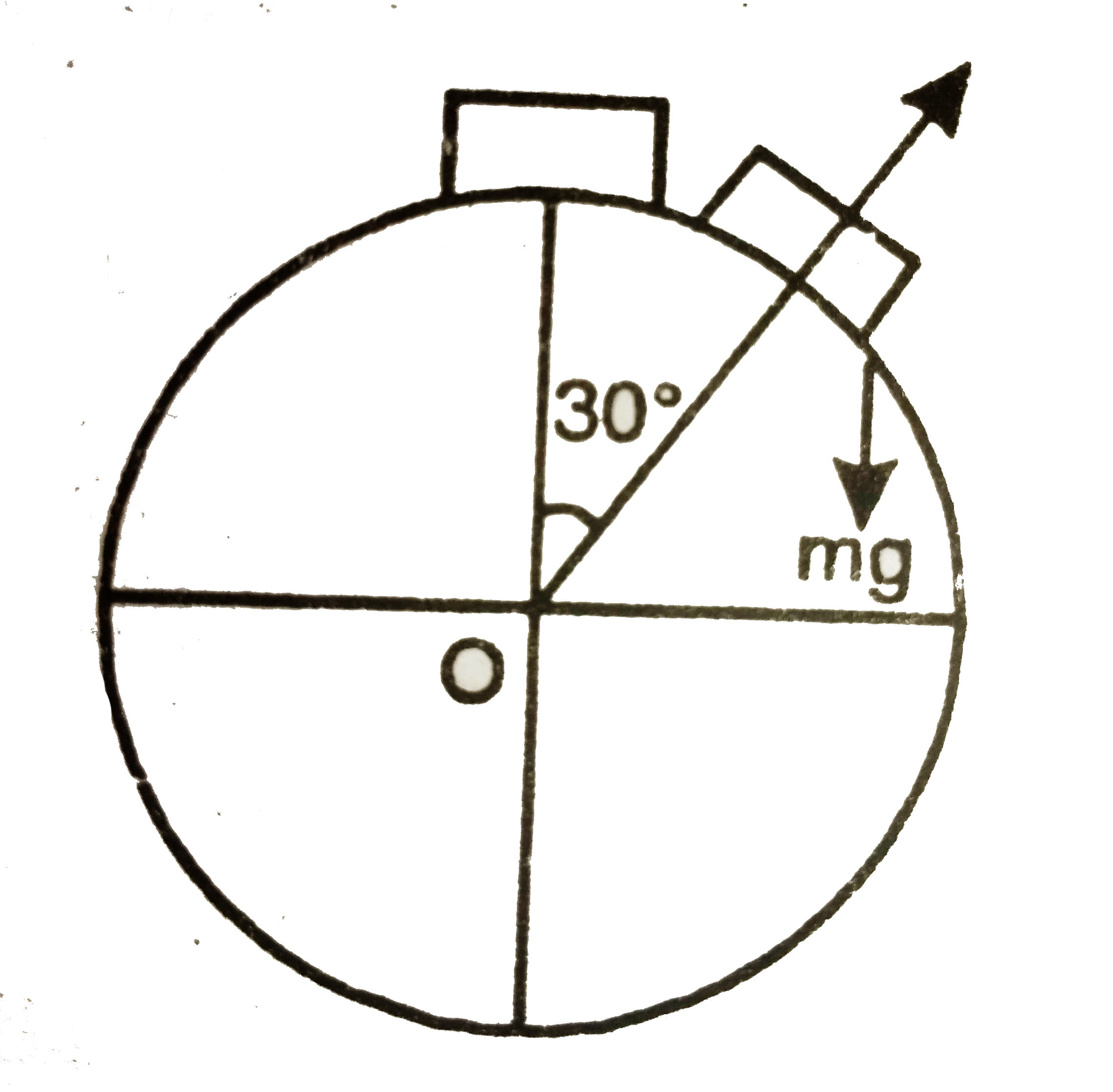Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
HC VERMA-ROTATIONAL MECHANICS-Exercises
- Suppose the platform with the kid in the previous problem is rotting i...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform rod of mass m and length l is struck at an end by a force F ...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform rod of length L lies on a smooth horizontal table. A particl...
Text Solution
|
- Suppose the particle of the previous problem has a mass m and a speed ...
Text Solution
|
- Two small bals A and B, each of mass m, are joined rigidlyl by a light...
Text Solution
|
- Two small balls A and B each of mass m, are joined rigidly to the end...
Text Solution
|
- Suppose the rod with the balls A and B of theprevious problem is clamp...
Text Solution
|
- Two blocks of masses 400 g and 200 g are connected through a light str...
Text Solution
|
- The pulley shown in figure has a radius of 20 cm and moment of inertia...
Text Solution
|
- A metre stick is is held verticaly with one end on a rough horizontal ...
Text Solution
|
- A metre stick weighing 240 g is pivoted at its upper end in such a way...
Text Solution
|
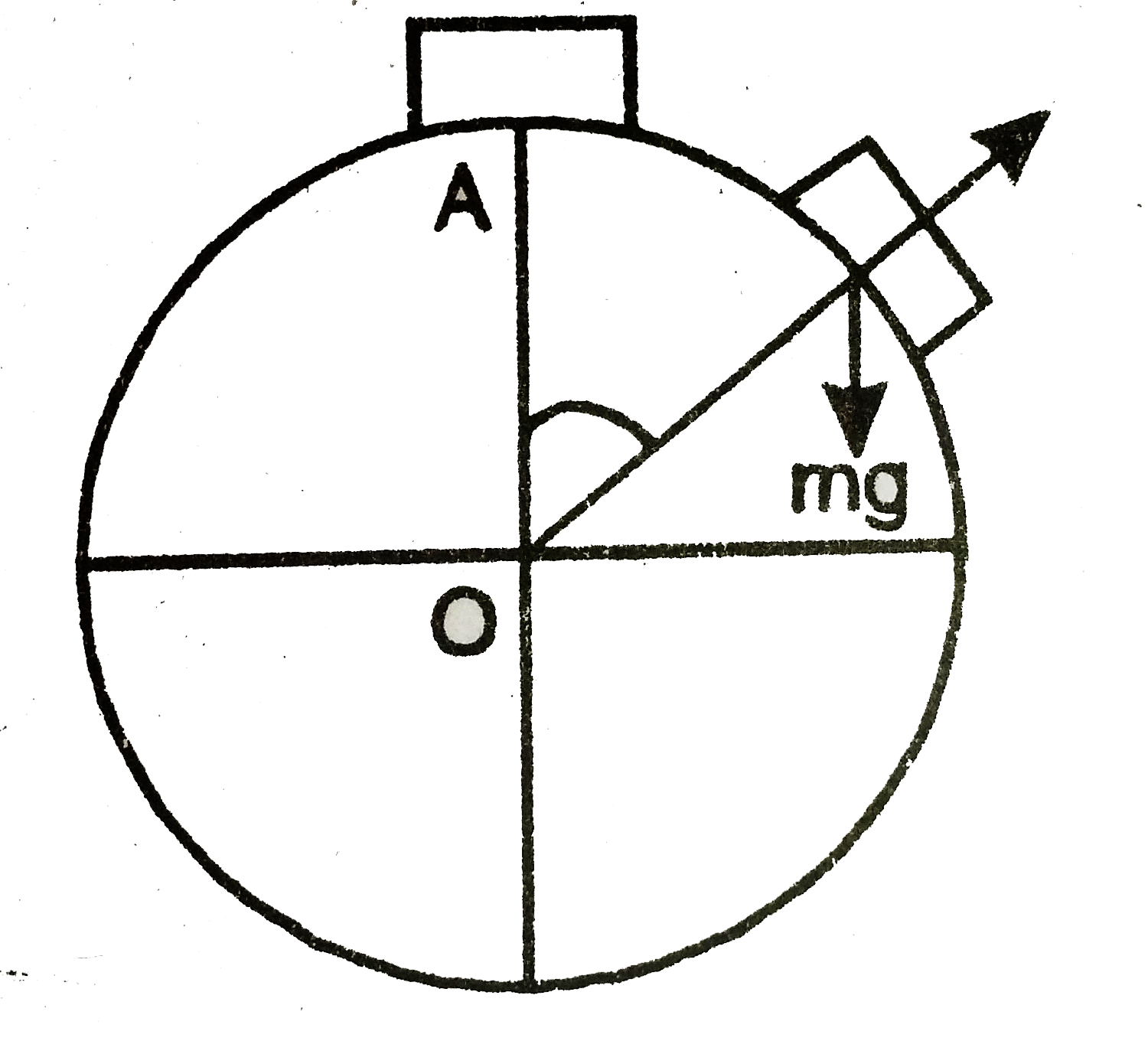
- A uniform rod pivoted at its upper end hangs vertically. It is displac...
Text Solution
|
- A cylinder rolls on a horizontal plane surface. If the speed of the ce...
Text Solution
|
- A sphere of mass m rolls on a plane surface. Find its kinetic energy a...
Text Solution
|
- A string is wrapped over the edge a uniform disc and the free end is f...
Text Solution
|
- A small spherical ball is released from a point at a height h on a rou...
Text Solution
|
- A small disc is set rolling with a speed v on the horizontal part of t...
Text Solution
|
- A sphere starts rolling down can incline of inclination theta. Find th...
Text Solution
|
- A hollow sphere is released from the top of an inlcined plane of incli...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the situation as shown in the figure. A solid sphere of mass ...
Text Solution
|