Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
HC VERMA-SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION-Exercises
- A rectangular plate of sides a and b is suspended from a ceiling by tw...
Text Solution
|
- A 1kg block is executing simple harmonic motion of amplitude 0.1 m on ...
Text Solution
|
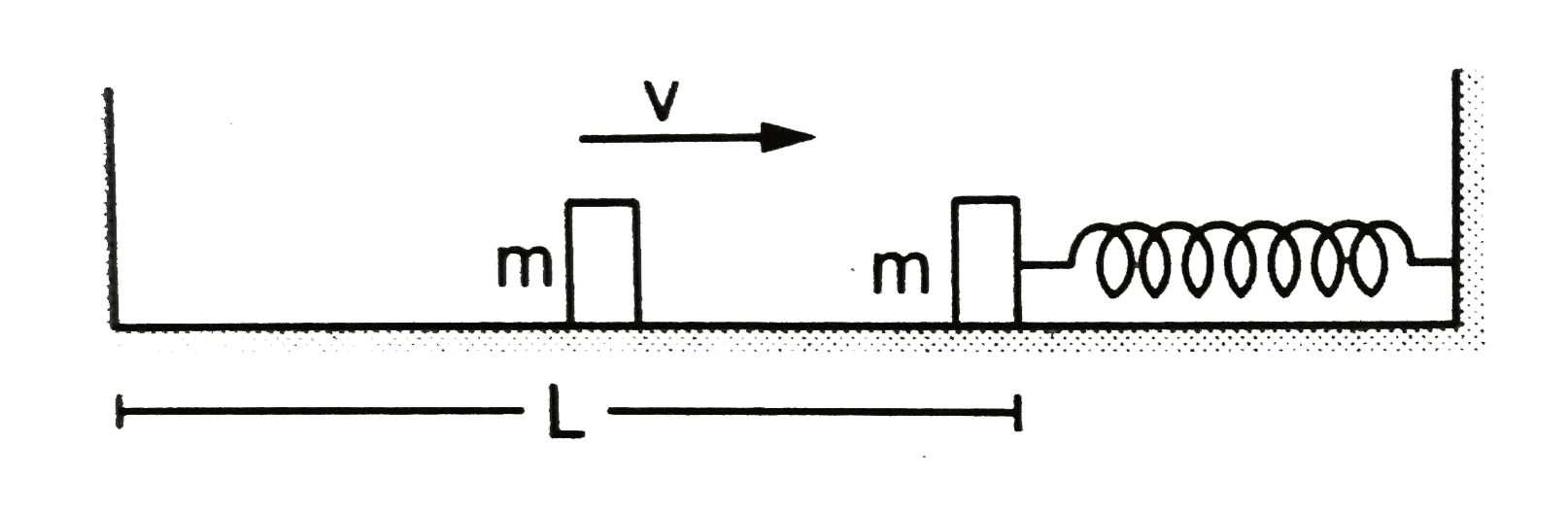
- The left block in figure moves at a speed v towards the right block pl...
Text Solution
|
- Find the time period of the motion of the particle shown in figure. Ne...
Text Solution
|
- All the surfaces shown in figure are frictionless. The mass of the car...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform table of mas M stays horizontally and symmetrically on two w...
Text Solution
|
- Find the length of seconds pendulum at a place where g =10 m/s^2.
Text Solution
|
- State the laws of simple pendulum.
Text Solution
|
- The pendulum of certain clock has time period 2.04 s. How fast or slow...
Text Solution
|
- A pendulum clock giving correct time at a place where g=9.800 ms^-2 is...
Text Solution
|
- A simple pendulum is constructed by hanging a heavy ball by a 5.0 m lo...
Text Solution
|
- The maximum tension in the string of an oscillating pendulum is double...
Text Solution
|
- A small block oscillates back and forth on as smooth concave surface o...
Text Solution
|
- A spherical ball of mass m and radius r rolls without slipping on a ro...
Text Solution
|
- The simple pendulum of length 40 cm is taken inside a deep mine. Assum...
Text Solution
|
- Assume that a tunnel is dug across the earth (radius=R) passing throug...
Text Solution
|
- Assume that a tunnel ils dug along a chord of the earth, at a perpendi...
Text Solution
|
- A simple pendulum of length l is suspended through the ceiling of an e...
Text Solution
|
- A simple pendulum of length 1 feet suspended from the ceiling of an el...
Text Solution
|
- A simple pendulum fixed in a car has a time period of 4 seconds when t...
Text Solution
|