Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
HC VERMA-LAWS OF THERMODYNAMICS-Short Answer
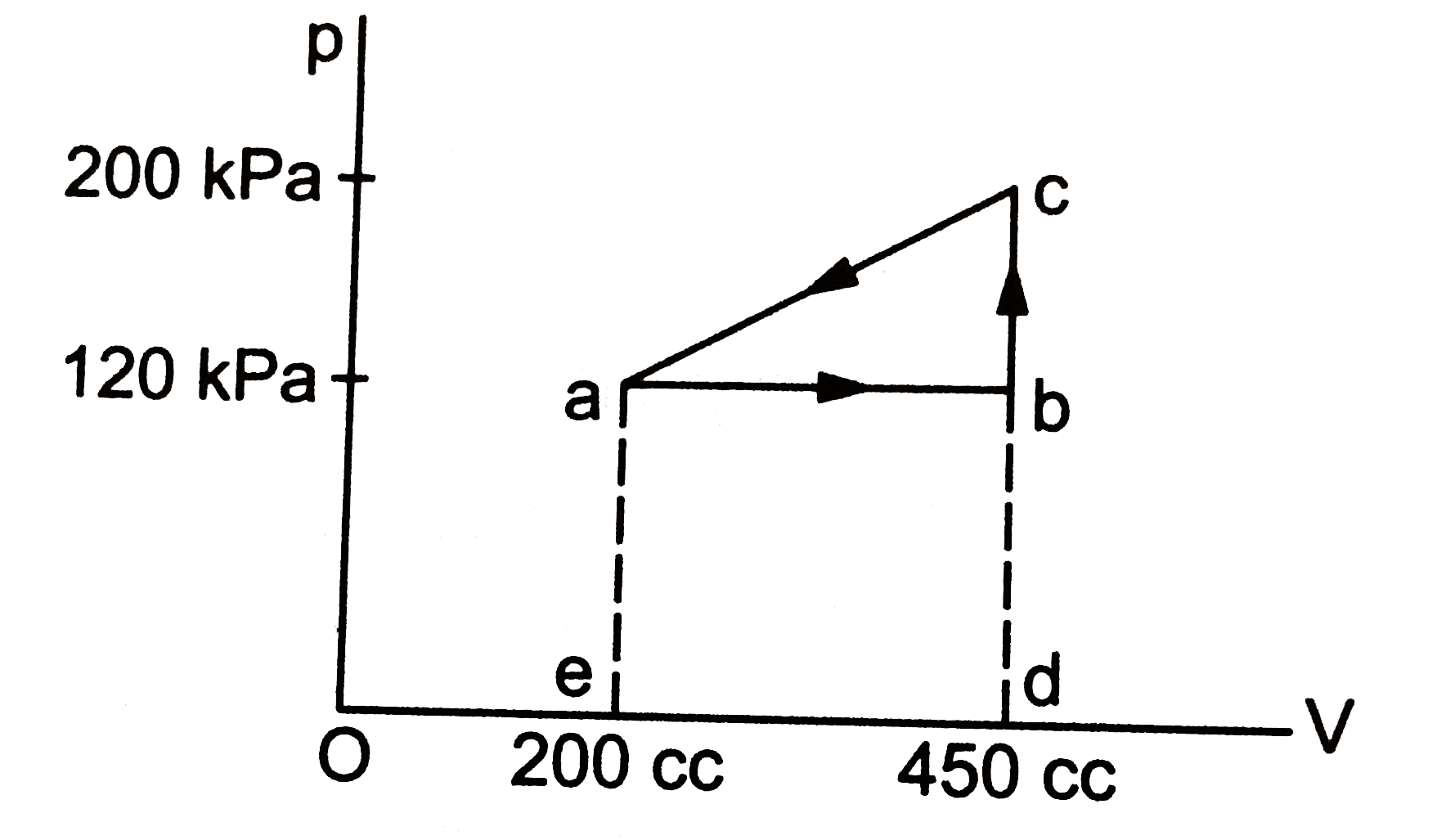
- calculate the work done by a gas as it is taken from the state a to b,...
Text Solution
|
- Should the internal energy of a system necessarily increase if heat is...
Text Solution
|
- Should the internal energy of a system necessarily increase if its tem...
Text Solution
|
- A cylinder containing a gas is lifted from the first floor to the seco...
Text Solution
|
- A force F is applied on a block of mass M. The block is displaced thro...
Text Solution
|
- When we rub our hands they become warm. Have we supplied heat to the h...
Text Solution
|
- A closed bottle contains some liquid. The bottle is shaken vigorously ...
Text Solution
|
- The final volume of a system is equal to the initial volume in a certa...
Text Solution
|
- Can work be done by a system without changing its volume?
Text Solution
|
- An ideal gas is pumped into a rigid container having diathermic walls ...
Text Solution
|
- When a tyre bursts, the air coming out is cooler than the surrounding ...
Text Solution
|
- When we heat an object, it expands. Is work done by the object in this...
Text Solution
|
- When we stir a liquid vigorously, it becomes warm. Is it a reversible ...
Text Solution
|
- What should be the condition for the efficiency of a carnot engine to ...
Text Solution
|
- When an object cools down, heat is withdrawn from it. Does the entropy...
Text Solution
|