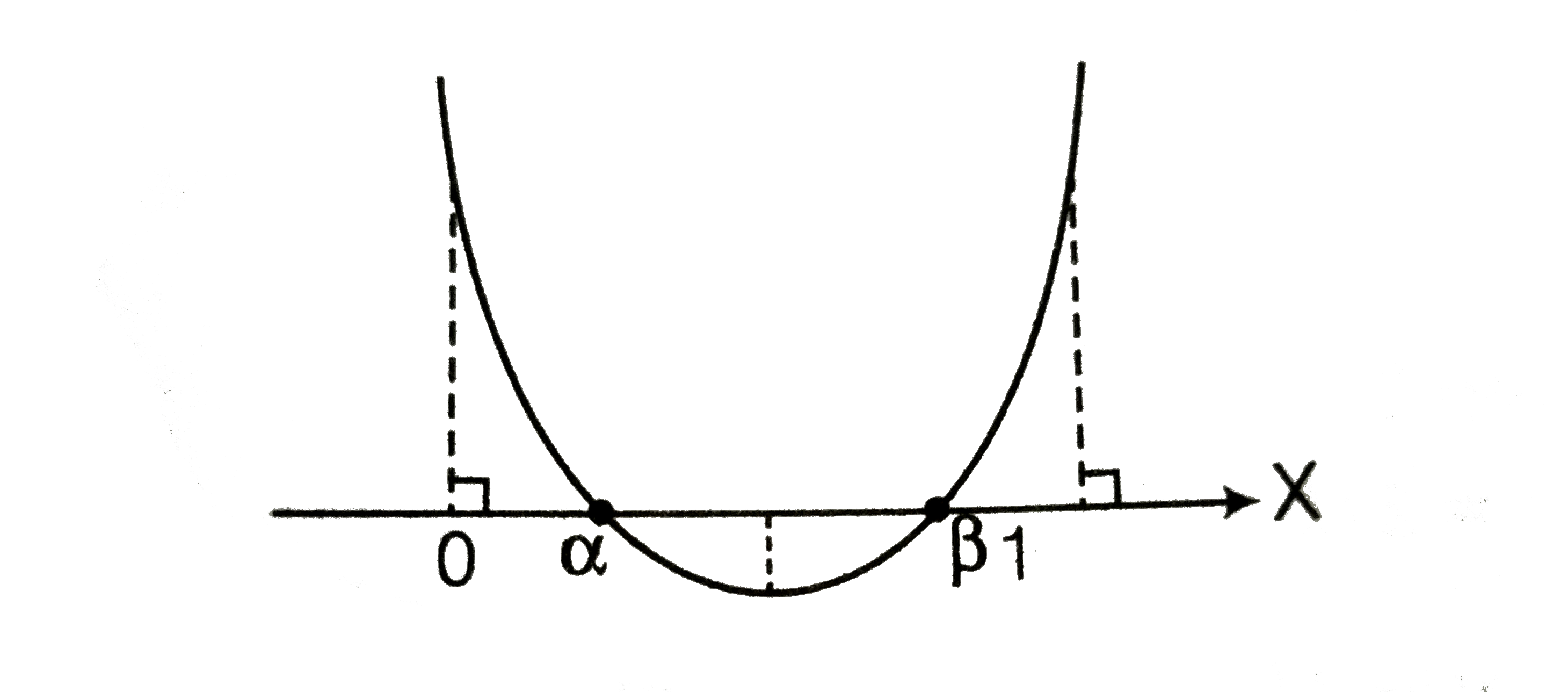
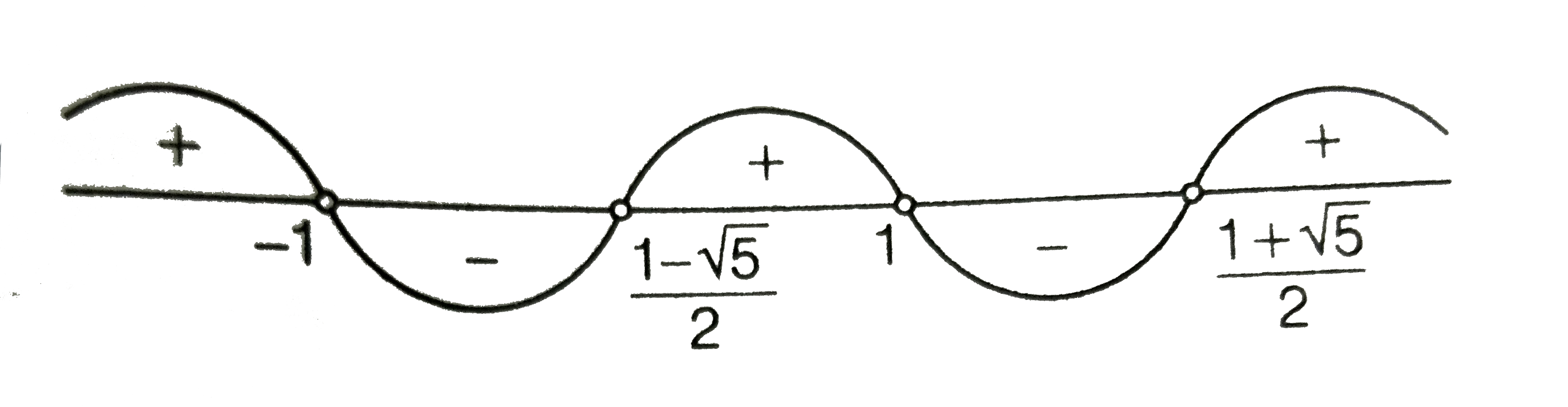
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- The value of a for which the equation (1-a^2)x^2+2ax-1=0 has roots bel...
Text Solution
|
- If t-1 and -t-1,t in R are the roots of (a+2)x^(2)+2ax-1=0, then compl...
Text Solution
|
- The values of 'K' for which the equation |x|^(2)(|x|^(2)2k+1)=1-k^(2),...
Text Solution
|
- If the roots of the equation 2ax^(3) + (3b-9) x + 1 = 0 are -2 and 3,...
Text Solution
|
- For what values of the parameter a the equation x^(4)+2ax^(3)+x^(2)+2a...
Text Solution
|
- Number of integral values of 'a' for which (a-5)x^2 - 2ax + (a-4)=0 , ...
Text Solution
|
- The equation x^4 + 2ax^3 + x^3 + 2ax + 1 = 0 has at least two distinct...
Text Solution
|
- The values of a for which both the roots of the equation (1-a^(2))x^(...
Text Solution
|
- If the equation x^(2)+2ax+b(a-1)=0 has real roots for all real value o...
Text Solution
|