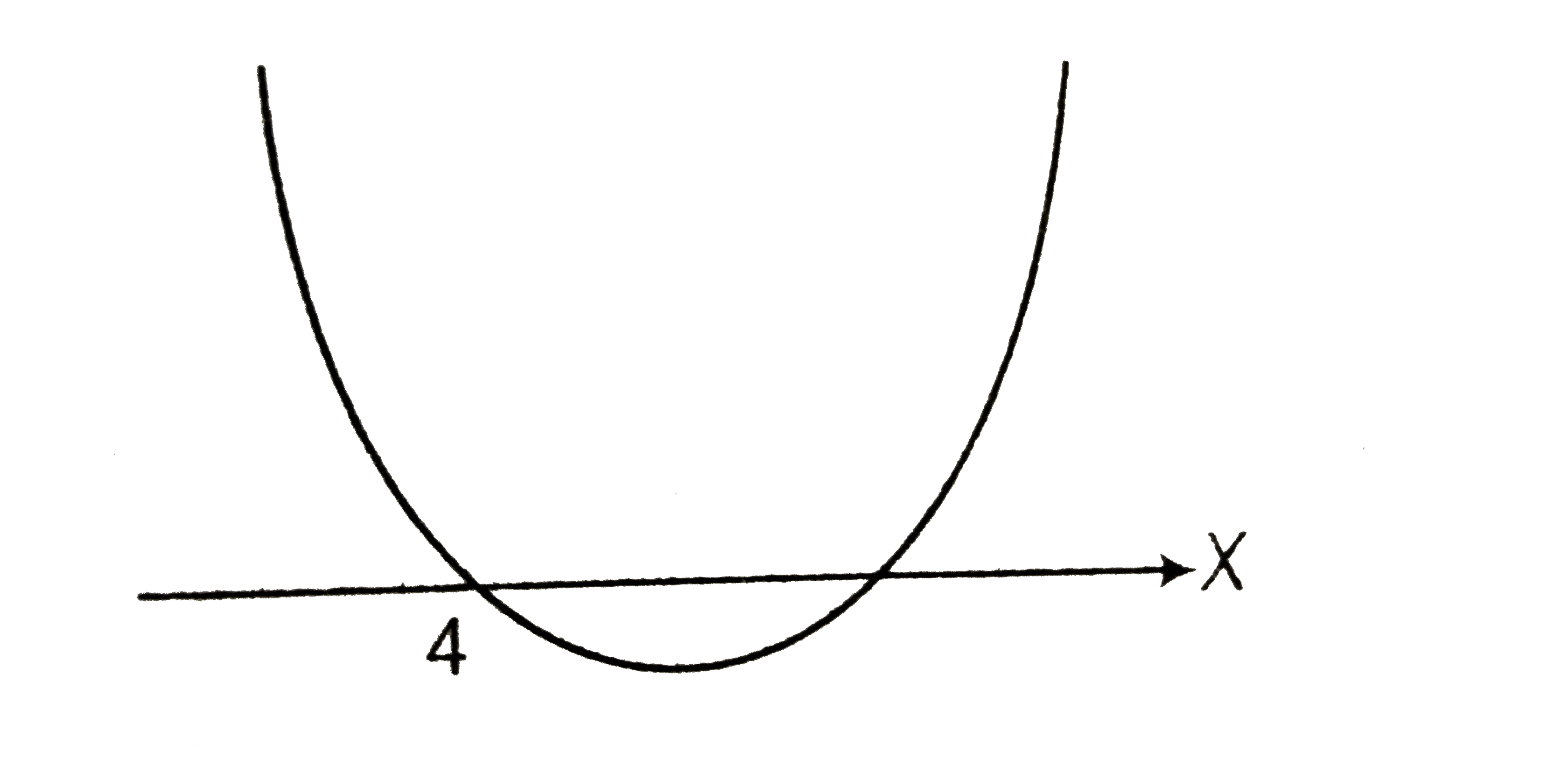
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- The smallest value of k for which both the roots of the equation x^(2)...
Text Solution
|
- The set of values of k(k in R) for which the equation x^(2)-4|x|+3-|k-...
Text Solution
|
- The positive value of k for which the equation x^2+k x+64=0 and x^2-8x...
Text Solution
|
- The smallest value of k, for which both the roots of the equation,x^(2...
Text Solution
|
- The smallest value of k for which both the roots of the equation x^(2)...
Text Solution
|
- The smallest value of k for which both the roots of the equation x^2-8...
Text Solution
|
- The value of k for which the equation (k-2) x^(2) + 8x + k + 4 = 0 has...
Text Solution
|
- The number of values (s) of k , for which both the roots of the equati...
Text Solution
|
- The positive value of k for which the equation x^2+k x+64=0 and x^2-8x...
Text Solution
|