A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
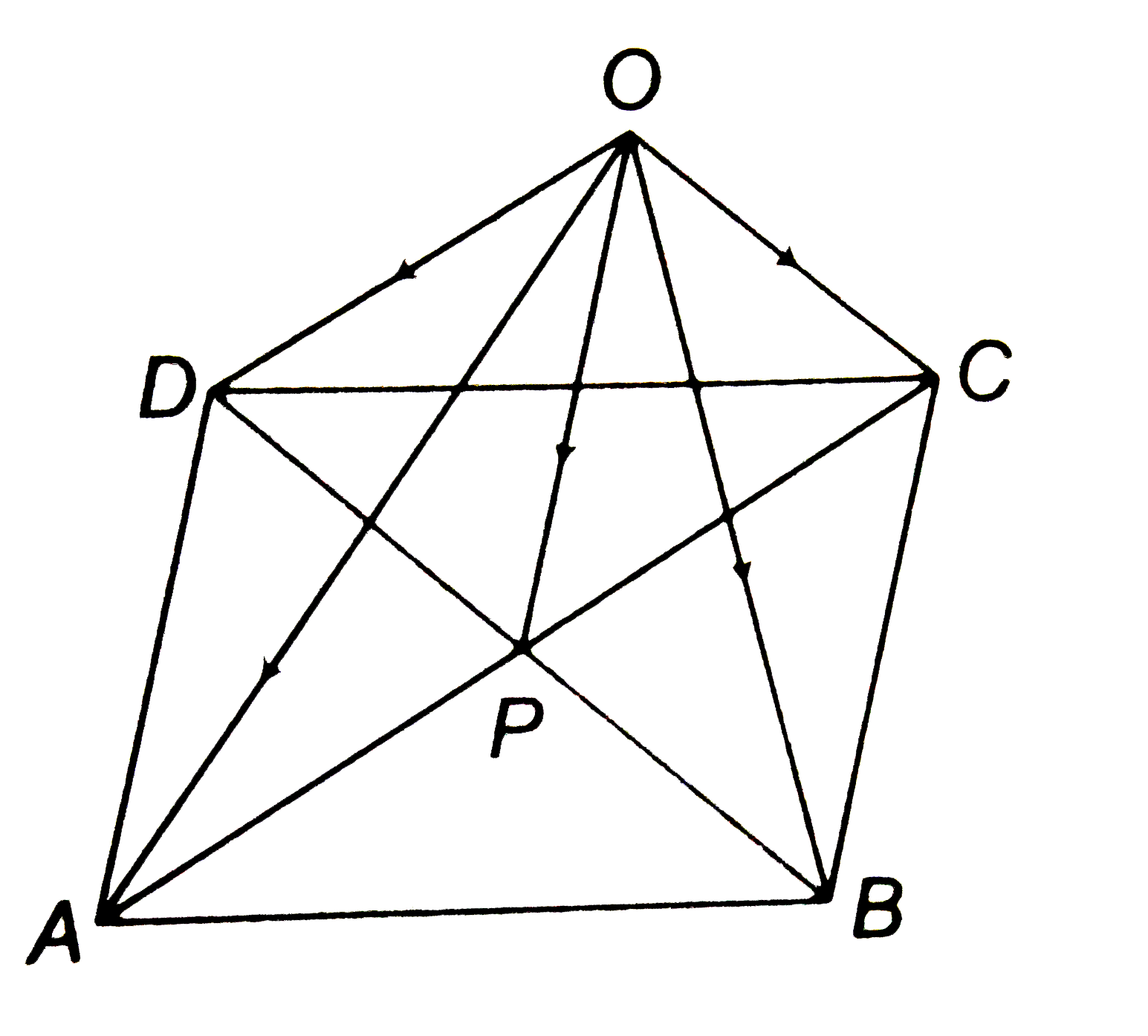
- ABCD is a parallelogram whose diagonals meet at P. If O is a fixed poi...
Text Solution
|
- A B C D is parallelogram and P is the point of intersection of its dia...
Text Solution
|
- Let A B C D be a p[arallelogram whose diagonals intersect at P and ...
Text Solution
|
- If A B C D is a rhombus whose diagonals cut at the origin O , then ...
Text Solution
|
- Given a regular hexagon ABCDEF with centre o,show that vec OB-vec OA=v...
Text Solution
|
- The magnitude of vectors vec(OA), vec(OB) and vec (OC) in figure are e...
Text Solution
|
- ABCD समान्तर चतुर्भुज के विकर्ण P पर मिलते है O कोई बिंदु है। सिद्ध क...
Text Solution
|
- ABCD एक समान्तर चतुर्भुज के विकर्ण P पर मिलते है, O कोई बिन्दु है। सिद...
Text Solution
|
- माना कि O समष्टभुज ABCDEF का केंद्र हैं, तो vec(OA) + vec(OB) + vec(...
Text Solution
|