A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
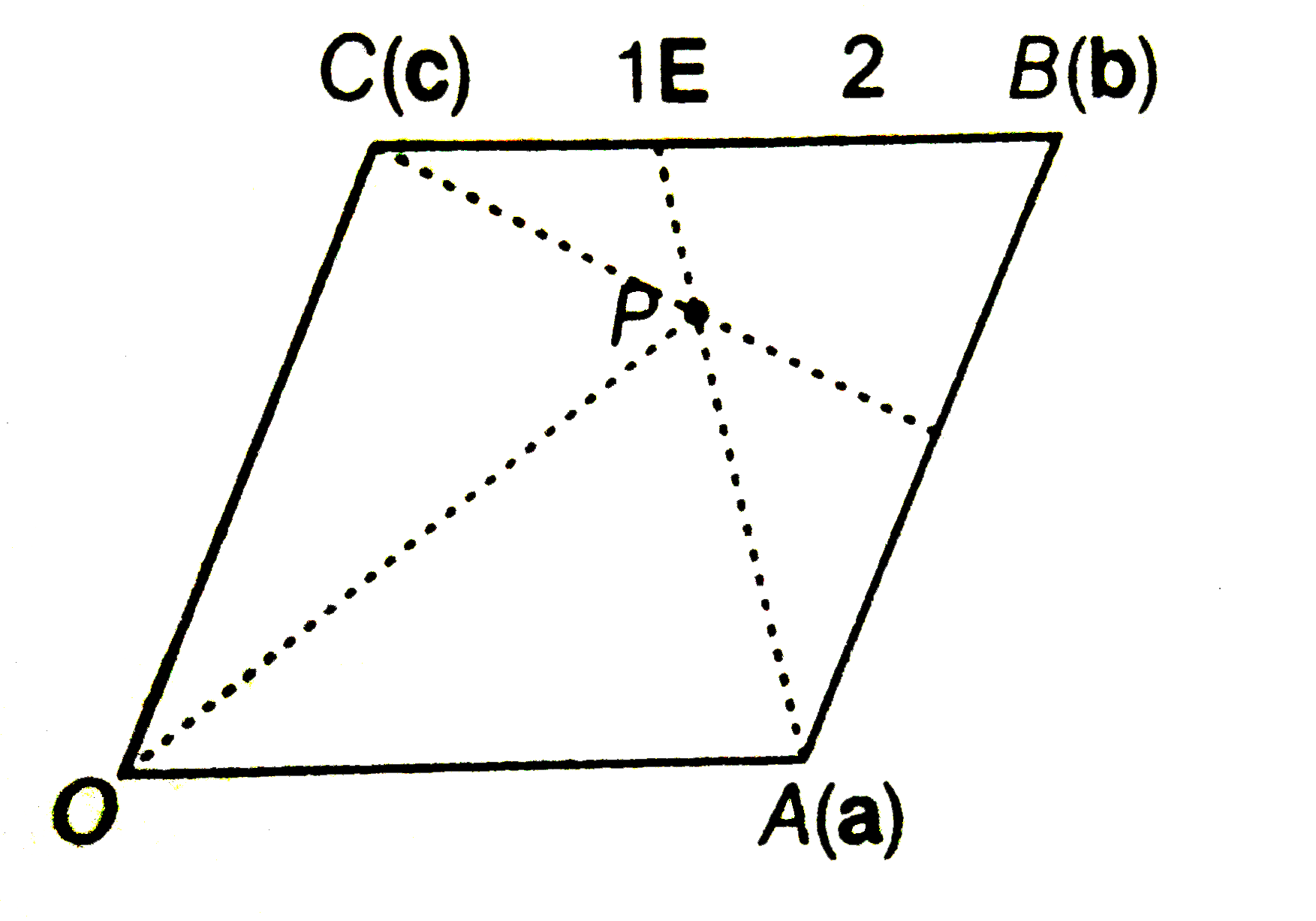
- In a parallelogram OABC vectors a,b,c respectively, THE POSITION VECTO...
Text Solution
|
- In a parallelogram OABC, vectors vec a, vec b, vec c are respectively ...
Text Solution
|
- In a parallelogram OABC, vectors veca, vecb, vecc are, respectively, t...
Text Solution
|
- In a parallelogram OABC, vectors veca, vecb, vecc are, respectively, t...
Text Solution
|
- In a parallelogram OABC vectors a,b,c respectively, THE POSITION VECTO...
Text Solution
|
- In a parallelogram OABC with position vectors of A is 3hat(i)+4hat(j) ...
Text Solution
|
- In a parallelogram OABC with position vectors of A is 3hat(i)+4hat(j) ...
Text Solution
|
- In a parallelogram OABC with position vectors of A is 3hat(i)+4hat(j) ...
Text Solution
|
- If the position vector of the poinot A is a+2b and a point P with posi...
Text Solution
|