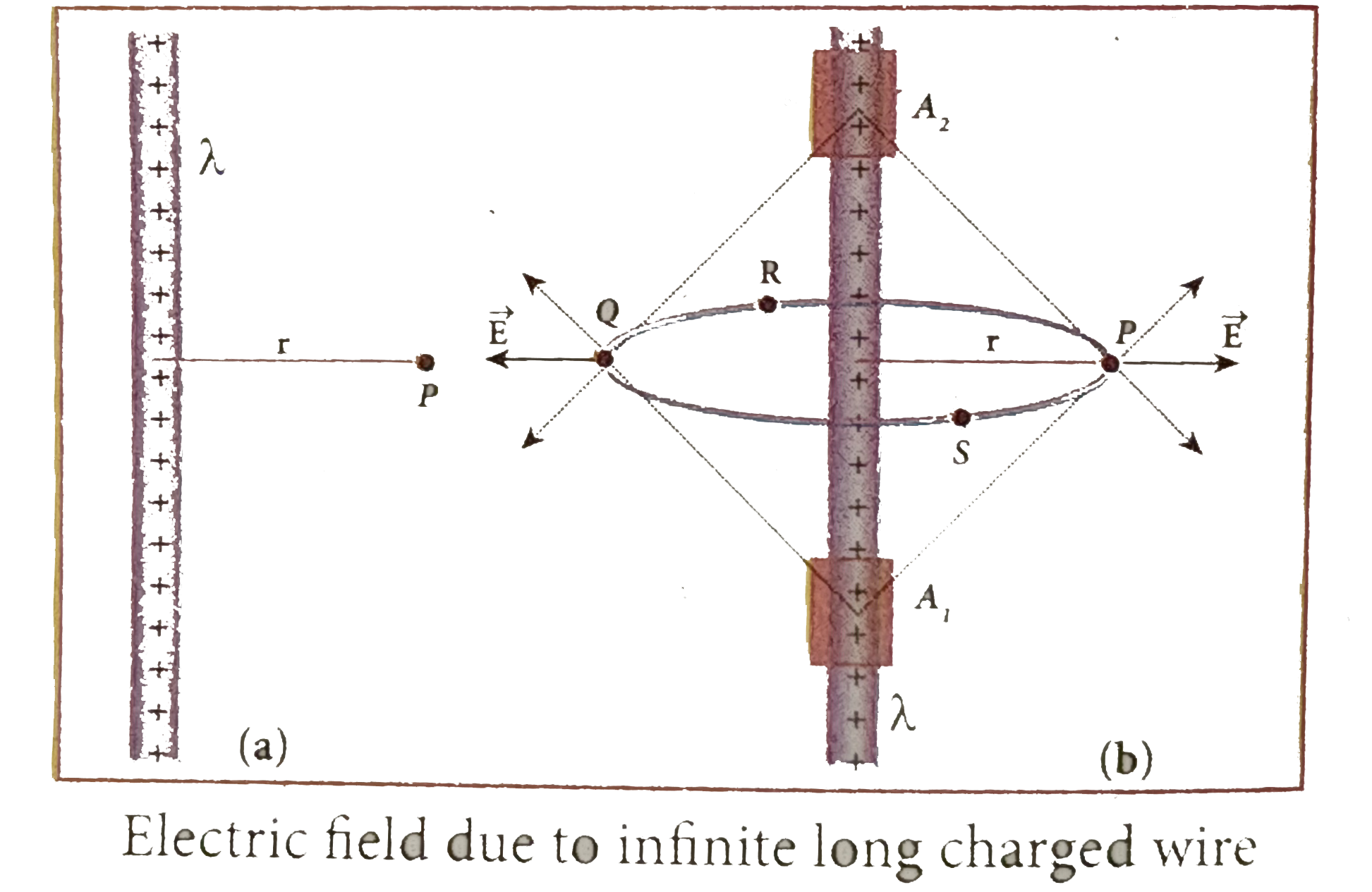
Consider an infinitely long straight wire having uniform linear charge density `lamda`. . Let P be a point located at a perpendicular distance r from the wire.
(ii) To find the electric field at the point P be two small charge elements `A_(1)andA_(2)` on the wire which are at requal distances from the point P are chooses.
(iii) The resultant electric field due to these two charge elements points radially away from the charged wire and the magnitude of electric field is same at all points on the circle of radius r.
(iv) The charged wire possesses a cylindrical symmetry, a cylindrical Gaussian surface of radius is r and length is L. The total electric flux in this closed surface E.
`Phi_(E)=ointvec(E).dvecA`
`underset("Curved surface")ointvec(E).dvecA+underset("top surface")ointvec(E).dvecA+underset("bottom surface")ointvecE.dvecA" ".........(1)`
(iv) for the curved surface, `vec(E)` is parallel to `vec(A)andvec(E).dvec(A)=EdA`. For the top and bottom surfaces, `vec(E)` is perpendicular to ` vec(A)` and `vec(E).dvec(A)=0`
Substituting these values in the equation (1) and applying Gauss law to the cylindrical surface,
`Phi_(E)=underset("Curved surface")(intE.dA)=(Q_(encl))/(epsi_(0))" ".........(2)`
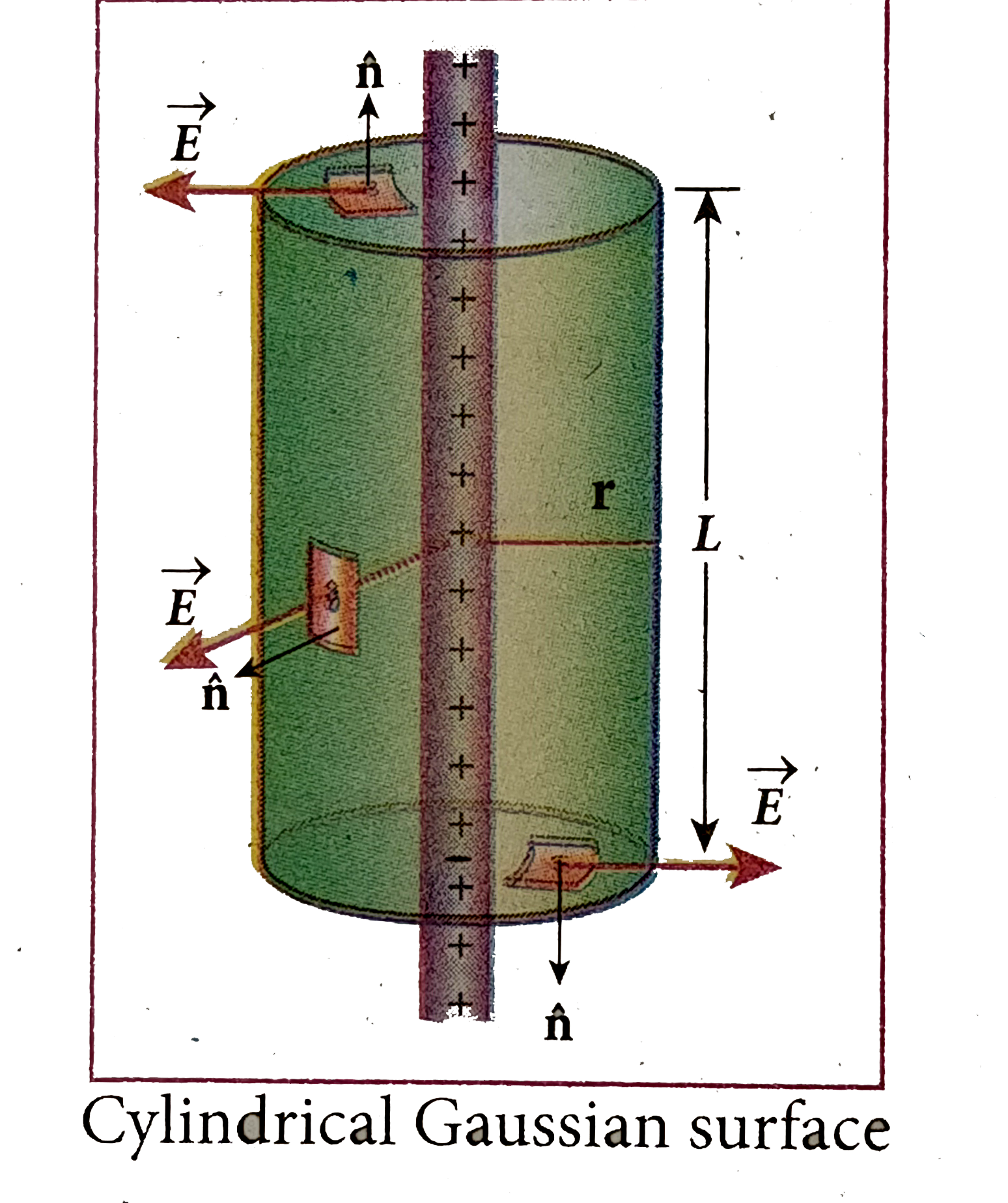
(v) Since the magnitude of the electric field for the entire curved surface is constant `Q_(encl)` is given by `Q_(encl)=lamdaL`.
`underset("Curved surface")(EintdA)=(lamdaL)/(epsi_(0))" ".........(3)`
Here `phiE=underset("Curved surface")(intdA)` total area of the curved
surface `=2pirl`. Substituting this in equation (3),
`E.2pirL=(lamdaL)/(epsi_(0))`
`E=(1)/(2piepsi_(0))(lamda)/(r)" "......(4)`
In vector form `vec(E)=(1)/(2piepsi_(0))(lamda)/(r)hatr" "............(5)`
(vi) The electric field due to the infinite charged wire depends on `(1)/(r)` rather that `(1)/(r^(2))` for a point charge. Equation (5) indicates that the electric field is always along the perpendicular direction `(hatr)` to wire. In fact, if `lamdagt0` then `vec(E)` points perpendicular outward `(hatr)` from the wire and if `lamdalt0`, then `vec(E)` points perpendicular inward `(-hatr)`.
(vii) The equation (5) is true only for an infintely long charged wire. For a charged wire of finite length the electric field need not be radial at all points. However, equation (5) for such a wire is taken approximately true around the mid-point of the wire and far away from the both ends of the wire.

