Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- The graph shows the variation of volatage 'v' across the plates of two...
Text Solution
|
- Shows the variation of voltage V across the plates of two capacitors A...
Text Solution
|
- The given graph in Fig. shows the variation of charge q versus potenti...
Text Solution
|
- The graph in Fig, shows variation of total energy U stored in the capa...
Text Solution
|
- A capacitor of unknown capacitance is connected across a battery of V ...
Text Solution
|
- दिये गये ग्राफ में एक संधारित्र की कुल संचित ऊर्जा (U ) तथा धारिता का ...
Text Solution
|
- चित्र में दो संधारित्रों A व B के लिए आवेश q तथा विभवांतर V के बीच ग्र...
Text Solution
|
- The graph shown here, shows the variation of the total energy ( E) sto...
Text Solution
|
- A few capacitors are equally charged. Which of the figures shows the n...
Text Solution
|
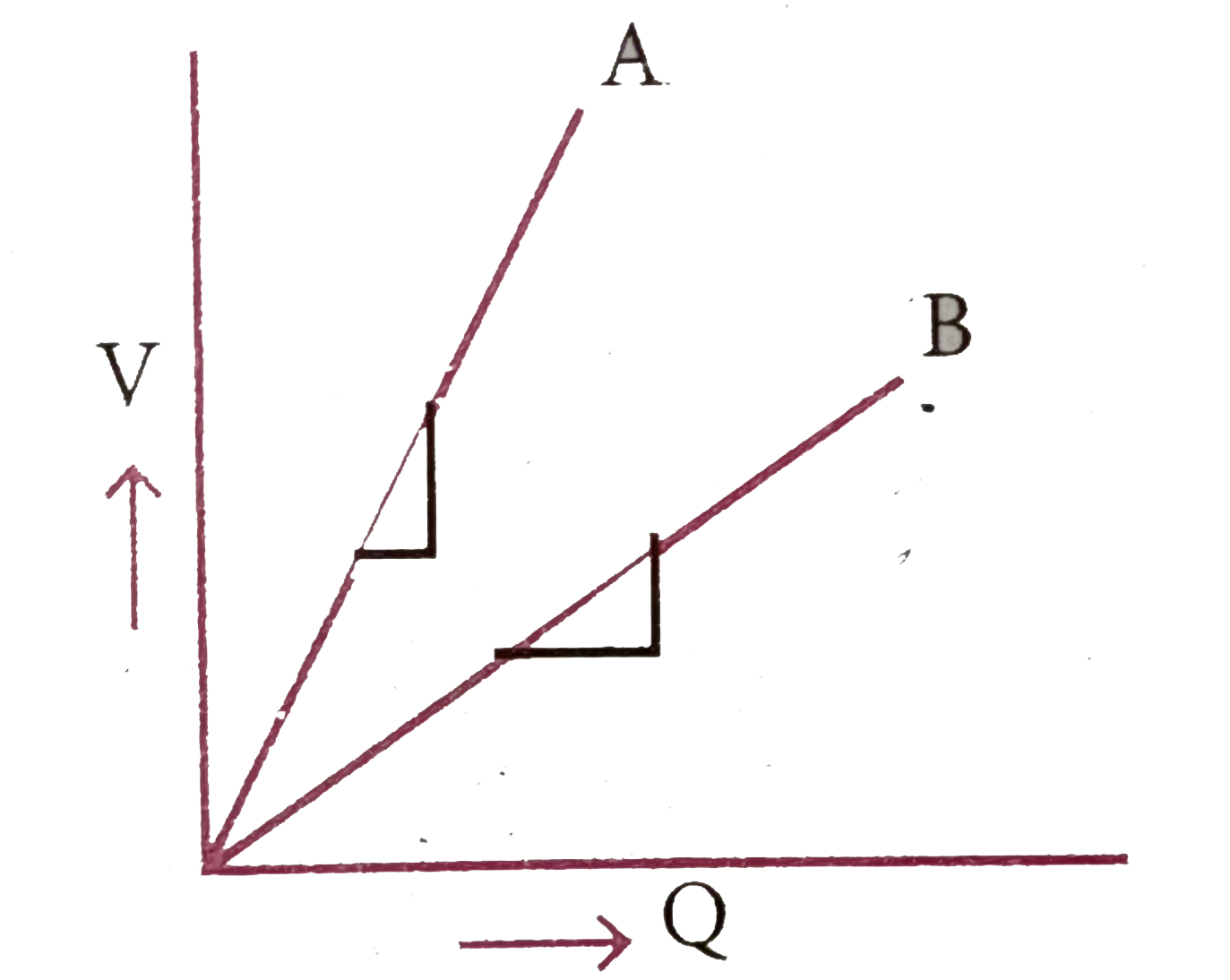 `C=(Q)/(V)=(1)/("slope")`
`C=(Q)/(V)=(1)/("slope")`