When dielectrics like mica, glass or paper are introduced between plates, then the capacitance is altered. The dielectric can be inserted into the plates in two different ways. (i) when the capacitor is disconnected from the battery. (ii) when the capacitor is connected to the battery.
(i) When the capacitor is disconnected form the battery: Let us consider a capacitor with two parallel plates each of cross-sectional area A and are separated by a distance d. The capacitor is charged by a battery of voltage `V_0` and the charge stored is `Q_0`. The capacitance of the capacitor without the dielectric is
`C_0 = Q_0/V_0`
The battery is then disconnected from the capacitor and the dielectric is inserted betwwen the plates.
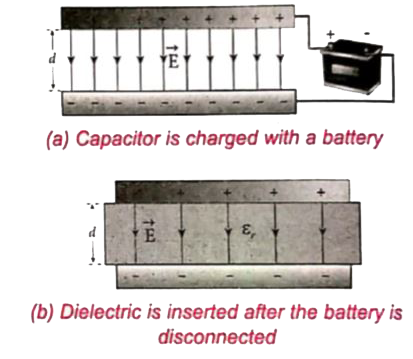
The induction of dielectric between the plates will decrease the electric field. Experimentally it is found that the modified electric field is given by
`E = E_0/epsilon_r`
Here `E_0` is the electric field inside the capacitors when there is no dielectric and `epsilon_r` is the relative permability of othe dielectric constant. Since `epsilon_r gt 1`, the electric field `E lt E_0`.
As a result, the electrostatic potential difference between the plates (V = Ed) is also reduced. But at the same time, the charge `Q_0` will remain constant once the battery is disconnected.
Hence the new potential difference is
`V= Ed = E_0/epsilon_rd = V_0/epsilon _r`
We know that capacitance is inversely proportional to the potential difference. Therefore as V devreases, C increases.
Thus new capacitance in the presence of a dielectric is
`C = Q_0/V = epsilon, Q_0/V_0 = epsilon_rC_0`
Since `epsilon_r gt 1`, we have `C gt C_0`. Thus insertion of the dielectric increases the capacitance.
Using equation
`C_0 = Q/V = Q/(((QD)/(Aepsilon_0)))= (epsilon_0A)/d`
`C = (epsilon_repsilon_0A)/d = (epsilonA)/d`
where `epsilon = epsilon_repsilon_0` is the permitivity of the dielectric medium. The energy stored in the cpacior before the inserton of a dielectric is given by
`U_0 = 1/2Q_0^2/C_0`
After the dielectric is inserted, the charge `Q_0` remains constant but the capacoitance is increased. As a result, the stored energy is decreased.
`U = 1/2Q_0^2/C_0 = 1/2Q_0^2/(epsilon_rC_0)=U_0/epsilon_r`
Since `epsilon_r gt 1` we get `U lt U_0`. There is a decrease in energy because, when the dielectric is inserted, the capacitor spends some energy in pulling the dielectric inside.
(ii) When the battery remains connected to the capacitor:
Let us consider what happens when the battery of voltage `V_0` remains connected to the capacitor when the dielectric is inserted into the capacitor.
The potential difference `V_0` across the plates remains constant. But it is found experimentally (first shown by faraday) that when dielectric is inserted, the charge stored in the capacitor is increased by a factor `epsilon_r`.

`Q = epsilon_rQ_0`
Due to this increased charge, the capacitance is also increased. The new capacitance is
`C = Q/V_0 = epsilon_rQ_0/V_0 = epsilon_rC_0`
Now, ` C_0 = (epsilon_00A)/d`
and ` C = (epsilonA)/d`
The energy stored in the capacitor before the insertion of a dielectric is given by
`U_0 = 1/2C_0V_0^2`
Note that here we have not used the expression
`U_0 = 1/2Q_0^2/C_0`
because here, both charge and capacitance are changed, whereas in above equation, `V_0` remains constant.
After the dielectric is inserted, the capacitance is increased, hence the stored energy is also increased.
`U = 1/2CV_0^2 = 1/2epsilon_rC_0V_0^2 = epsilon_rU_0`
Since `epsilon_r gt 1` we have `U gt U_0`
It may be noted the capacitor `V_0` is constant, the electric field between the plates also remains constant.
The energy density is given by
`U = 1/2 epsilonE_0^2`
where `epsilon` is the permitivity of the given dielectric material.

