Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
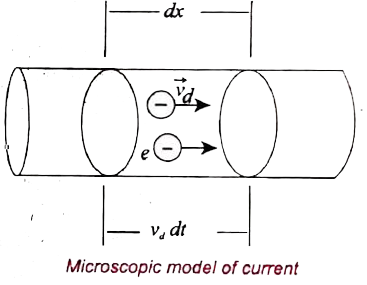
- Describe the microscopic model of current and obtain general from of O...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion: Ohm's law is not valid if current depends on voltage non-li...
Text Solution
|
- ओम के नियम के अनुसार विभवान्तर व धारा के बीच ग्राफ होगा एक -
Text Solution
|
- ओम के नियम के अनुसार विभवान्तर व धारा के बीच ग्राफ होगा एक
Text Solution
|
- Describe Holliday model for general recombination
Text Solution
|
- Describe the microscopic model of current and obtain general from of O...
Text Solution
|
- Obtain the macrscopic form of Ohm's law form its microscopic form and ...
Text Solution
|
- State macroscopic form of Ohm's law.
Text Solution
|
- Obtain the macrscopic form of Ohm's law form its microscopic form and ...
Text Solution
|