Foucault currents are used in :
(i) Induction stove
(ii) Eddy current brake
(iii) Eddy current testing
(iv) Electromagnetic damping
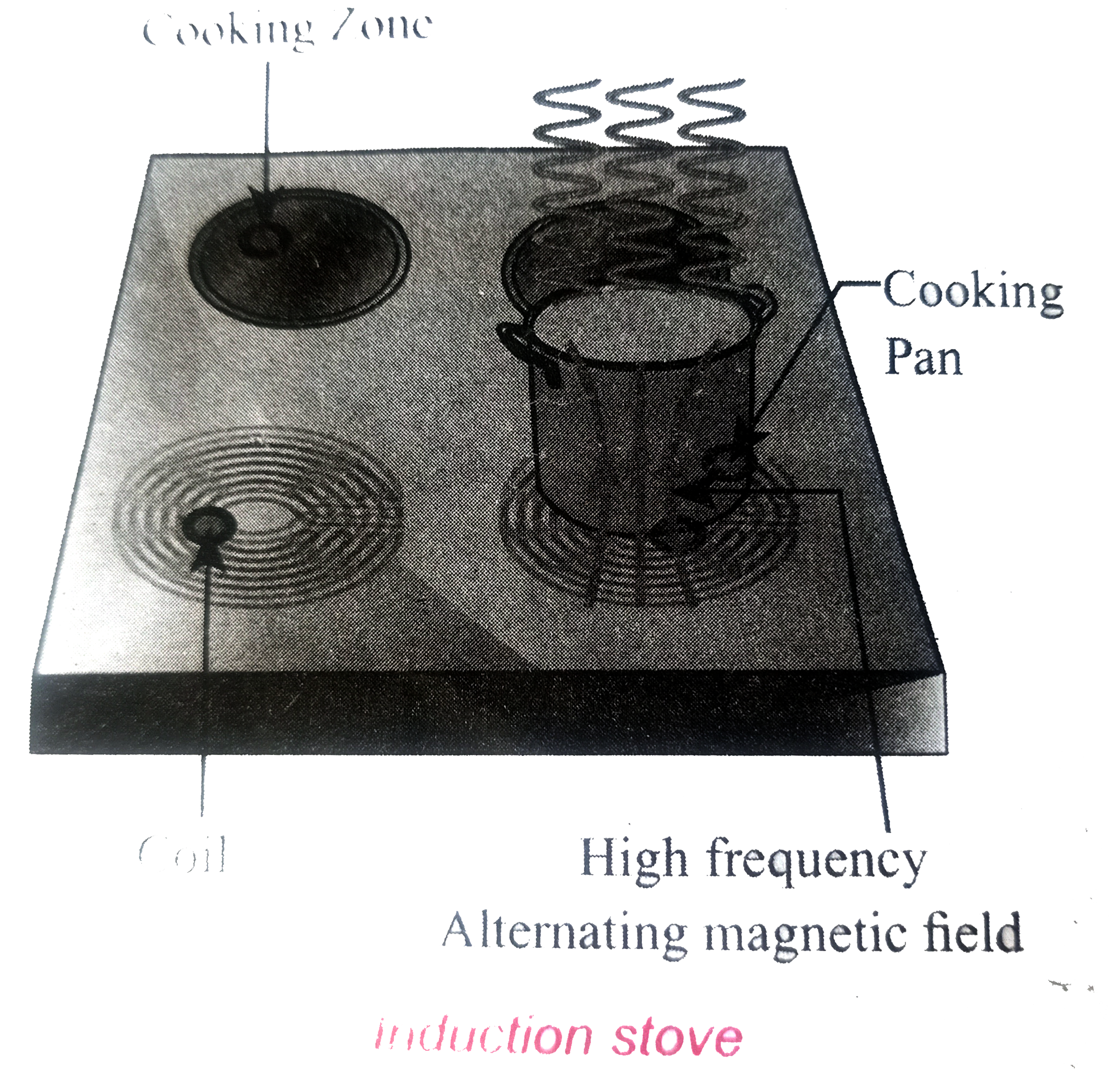
Induction stove is used to cook the food quickly and safely with less energy consumption. Below the cooking zone,there is a tighty wound coil of insulated wire . The cooking pan made of suitable material, is placed over the cooking zone. When the stove is switched on, an alternating current flowing in the coil produces high frequency alternating magnetic field which induces very strong eddy current in the cooking pan. The eddy current in the pan produce so much of heat due to Joule heating which is used to cook the food.
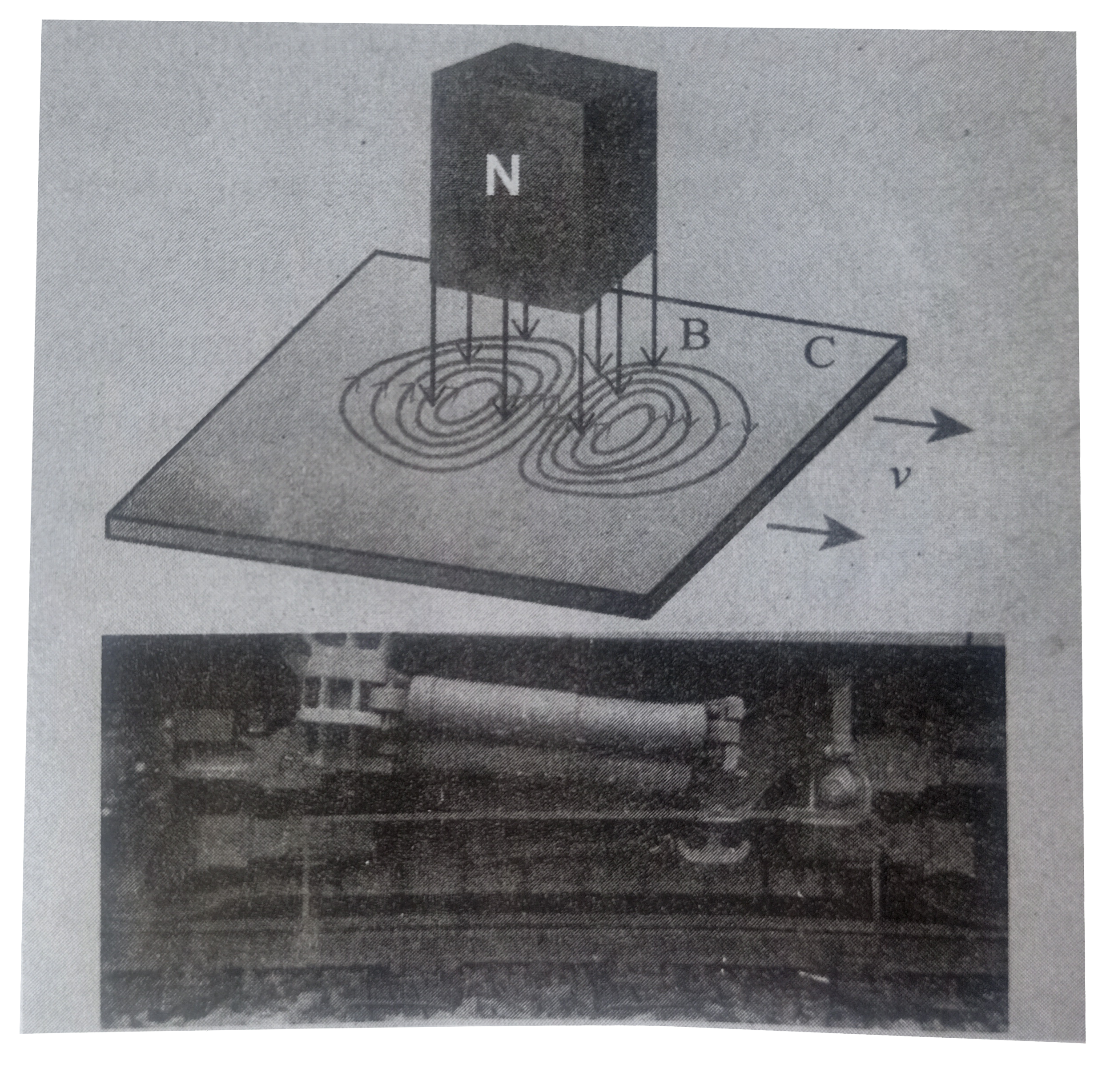
Eddy current brake: This eddy current braking system is generally used in high speed trains and roller coasters. Strong electromagnets are fixed just above the rails. To stop the train, electromagnets are switched on. The magnetic field of these magnets induces eddy current in the rails which oppose or resist the movement of the train.
In some cases, the circular disc, connected to wheel of the trains through a common shaft is made to rotate in between the poles of an electromagnet. When there is a relative motion between the disc and the magnet, eddy currents are induced in the disc which stops the train.
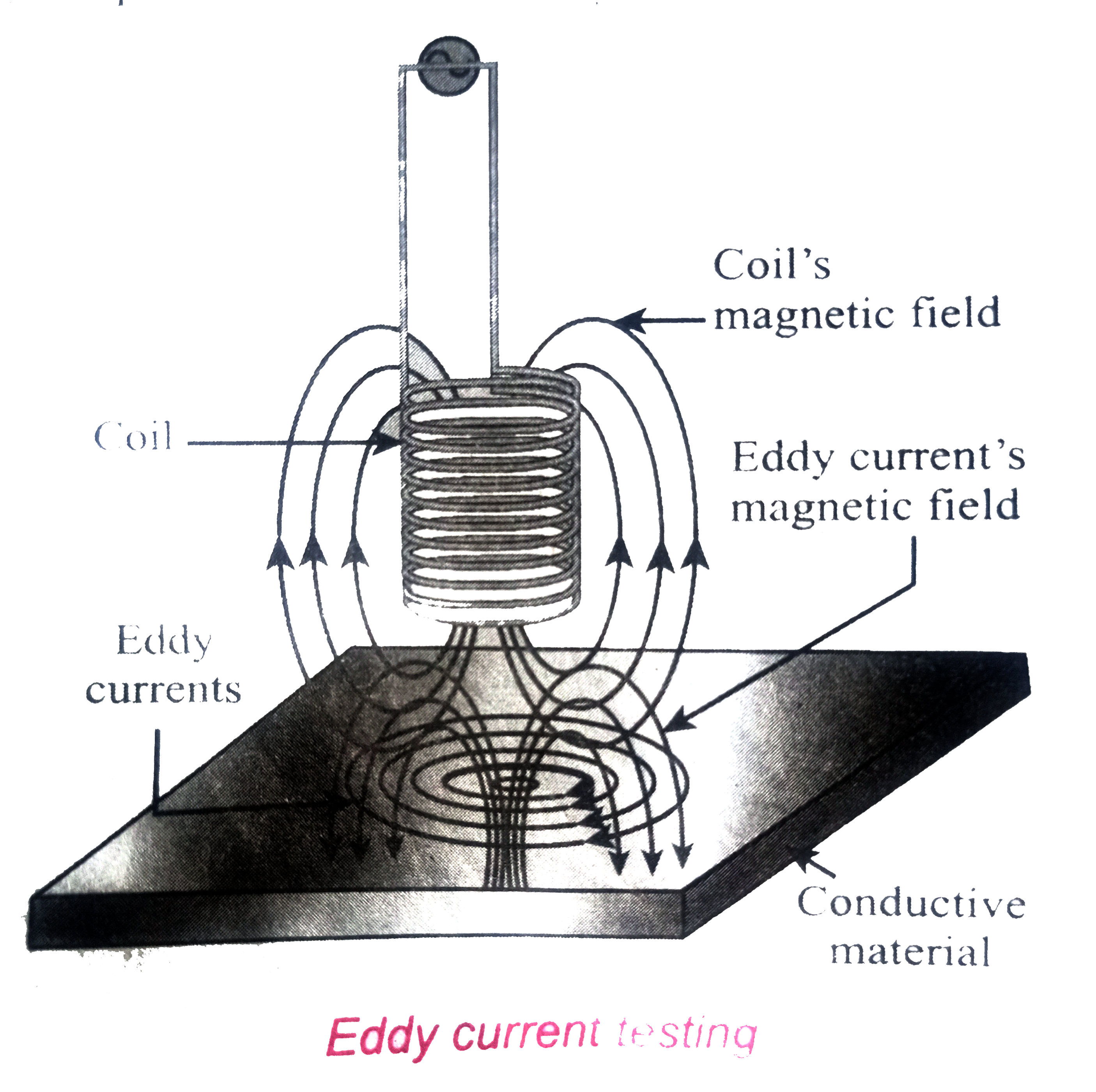
Eddy current testing : It is one of the simple non-destructive testing methods to find defects like surface crackes, air bubbles present in a specimen. A coil of insulated wire given an alternating electric current so that it produces an alternating magnetic field. when this coil is brought near the test surface, eddy current is induced in the test surface. The presence of defects causes the change in phase and amplitude of the eddy current that can be detected by some other means. In this way, the defects present in the specimen are identified.
Electro megnetic damping: The armature of the galvanometer coil is woud on a soft iron cylinder. Once the armature is deflected, the relative motion between the soft iron cylinder and the radial magnetic field induces eddy current in the cylinder.
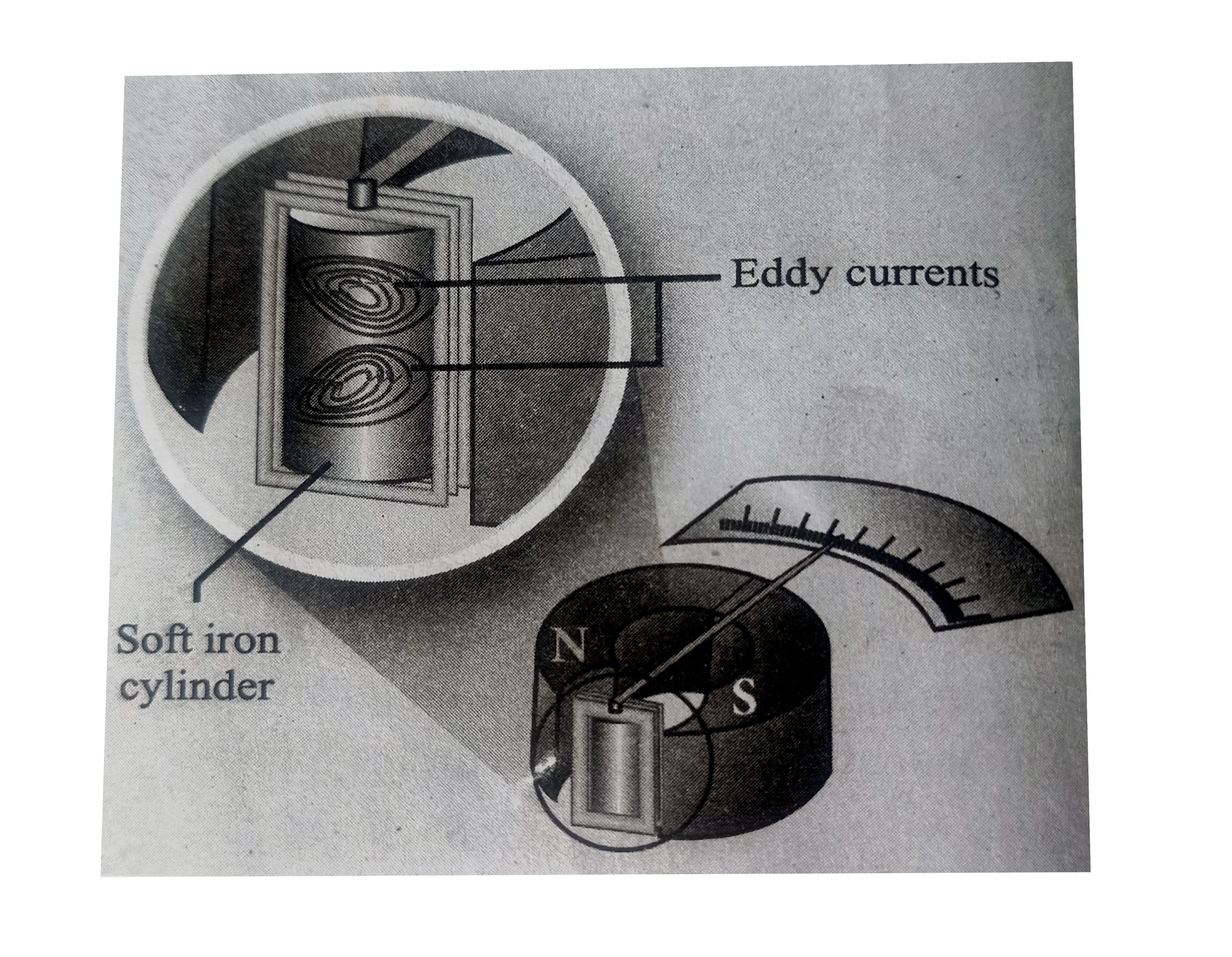
The damping force due to the flow of eddy current brings the armature to rest immediately and then galvanometer shows a steady deflection. This is called electromagnetic damping.



