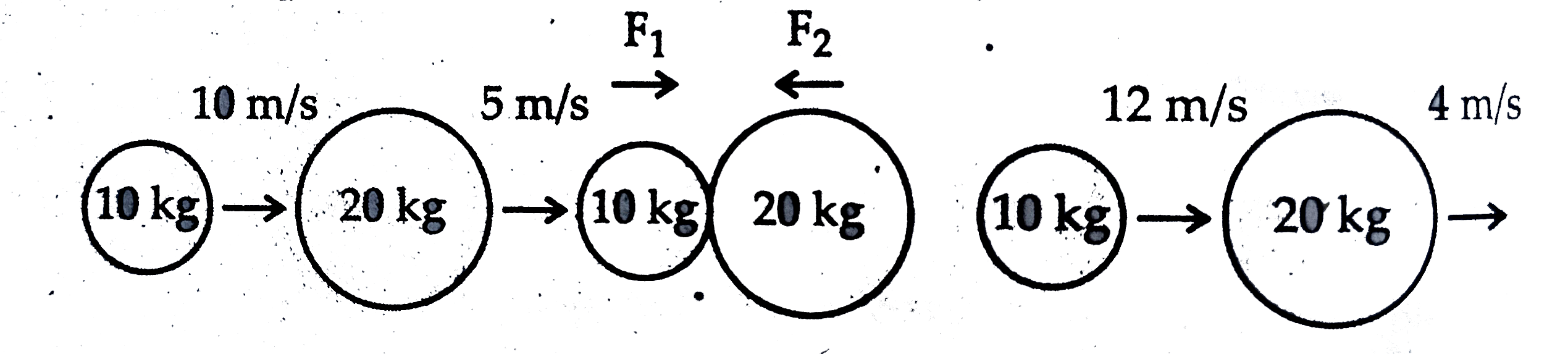Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- The figure represents two bodies of masses 10 kg and 20 kg, moving wit...
Text Solution
|
- A 10 kg ball and 20 kg ball approach each other with velocities 20 ...
Text Solution
|
- A ball of mass 1 kg moving with a velocity of "0.4 ms"^(-1) collides w...
Text Solution
|
- A body of mass 2 kg moving with uniform velocity of 40 ms^(-1) collide...
Text Solution
|
- A body of mass 5 kg moving on a horizontal surface with a velocity of ...
Text Solution
|
- A body of mass 5 kg moving on a horizontal surface with a velocity of ...
Text Solution
|
- A body of mass 5 kg moving on a horizontal surface with a velocity of ...
Text Solution
|
- Two perfectly elastic spheres of masses 2 kg and 3 kg moving in opposi...
Text Solution
|
- Two spheres A and B moving in opposite directions have velocities of 1...
Text Solution
|