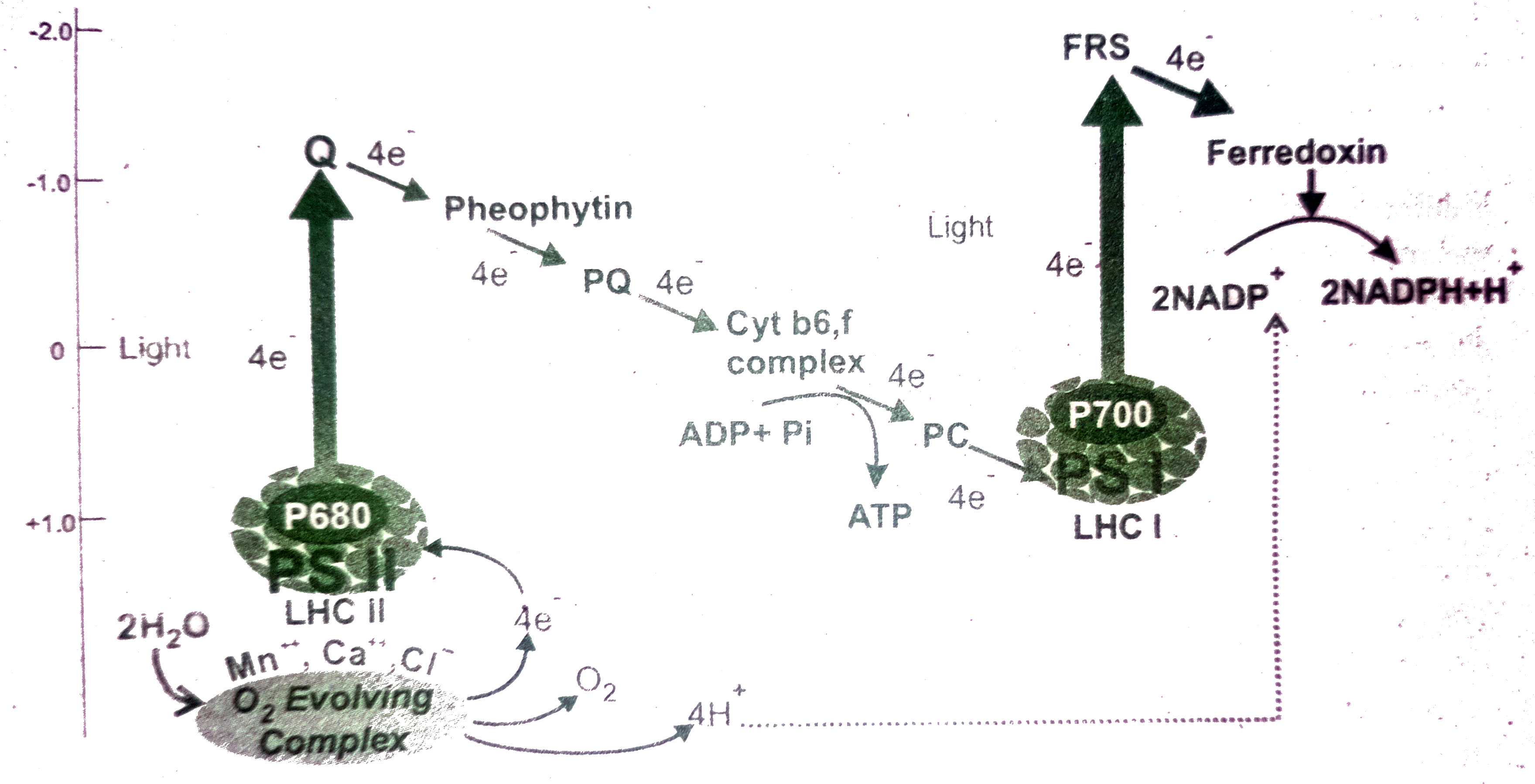
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
PHOTOSYNTHESIS
PREMIERS PUBLISHERS|Exercise Other Important Questions & Answers CHECK YOUR GRASP |3 VideosPHOTOSYNTHESIS
PREMIERS PUBLISHERS|Exercise Other Important Questions & Answers -III. Answer the following. (3 Marks)|12 VideosNEURAL CONTROL AND CO-ORDINATION
PREMIERS PUBLISHERS|Exercise SOLUTION TO TEXTUAL QUESTIONS(Text Book Page No. 71)|1 VideosPLANT GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT
PREMIERS PUBLISHERS|Exercise OTHER IMPORTANT QUESTIONS & ANSWERS (ANSWER THE FOLLOWING) (5 MARKS) |8 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
PREMIERS PUBLISHERS-PHOTOSYNTHESIS-Other Important Questions & Answers IV. Answer the following. (5 Marks)
- Explain in detail about absorption spectrum and action spectrum of lig...
Text Solution
|
- Distinguish between Photo system-I and photo system-II.
Text Solution
|
- Explain the process of photolysis of water with suitable diagram.
Text Solution
|
- Explain non-cyclic photophosphorylation.
Text Solution
|
- Explain chemiosmotic theory with suitable diagram.
Text Solution
|
- Compare and contrast the photosynthetic processes in C3 and C4 plants.
Text Solution
|
- Give the schematic diagram of photorespiration.
Text Solution
|
- Differentiate photorespiration and Dark respiration.
Text Solution
|