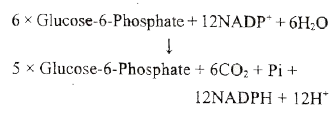During respiration breakdown of glucose in cytosol occurs both by glycolysis (about `2//3`) as well as by oxidative pentose phosphate pathway (about `1//3`). Pentose phosphate pathway was described by warburg, Dickens and Lipmann (1938). Hence, it is also called warburg-Dickens-Lipmann pathway. It takes place in cytoplasm of mature plant cells. It is an alternate way for breakdown of glucose.
It is also known as Hexose monophosphate shunt (HMP Shunt) or Direct Oxidative Pathway. It consists of two phases, oxidative phase and non-oxidative phase. The oxidative events convert six molecules of six carbon Glucose-6-phosphate to 6 molecules of five carbon sugar Ribulose-5 phosphate with loss of `6CO_2` molecules and generation of 12 `NADPH + H^(+)` (not NADH). The remaining reactions known as non-oxidative pathway, convert Ribulose-5-phosphate molecules to various intermediates such as Ribose-5-phosphate(5C), Xylulose-5-phosphate(5C) G l y c e r a l d e h y d e - 3 - p h o s p h a t e (3 C), Sedoheptulose - 7 - phosphate (7C), and Erythrose - 4 - phosphate (4C). Finally, five molecules of glucose - 6 - phosphate is regenerated. The overall reaction is:
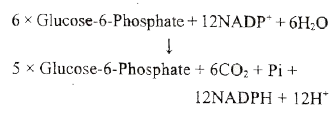
The net result of complete oxidation of one glucose -6- phosphate yield `6CO_(2)` and `12 NADPH + H^(+)` . the oxidative pentose phosphate pathway is controlled by glucose - 6- phosphate dehydrogenase enzyme which is inhibited by high ratio of NADPH to `NADP^(+)`.