Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
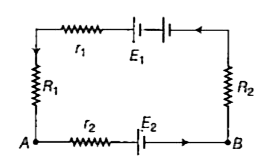
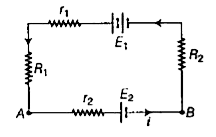
- If E(1) = 10 V, E(2) = 5V(1),r(1) = 0.1 Omega , r(2) = 0.1 Omega , R(1...
Text Solution
|
- In the network shown the potential difference between A and B is (R = ...
Text Solution
|
- In the circuit shown below E(1) = 4.0 V, R(1) = 2 Omega, E(2) = 6.0 V,...
Text Solution
|
- In the circuit in figure emf E(1) = 14V (internal resistance r(1) = 1O...
Text Solution
|
- In the circuit in figure emf E(1) = 14V (internal resistance r(1) = 1O...
Text Solution
|
- In the circuit R(1) = 4 Omega , R(2) = R(3) = 15 Omega R(4) = 30 Omega...
Text Solution
|
- Find a potentail difference varphi(1) - varphi(2) between points 1 and...
Text Solution
|
- Find the current flowing through the resistance R(1) of the circuit sh...
Text Solution
|
- In the circuit shown in the figure R(1) =3 Omega,R(2) = 2 Omega and R(...
Text Solution
|