Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
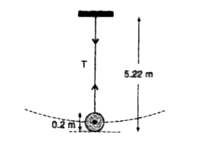
- A sphere of radius 0.1 m and mass 8pi kg is attached to the lower end ...
Text Solution
|
- A sphere of radius 0.1m and mass 8 pi kg is attached to the lower end ...
Text Solution
|
- A sphere of radius 10 cm and mass 25 kg is attached to the lower en...
Text Solution
|
- A sphere of radius 0.1m and mass 8 pi kg is attached to the lower en...
Text Solution
|
- A sphere of mass 2 kg and diameter 4.5 cm is attached to the lower and...
Text Solution
|
- A sphere of mass 25 kg and radius 0.1 m is hung from the celling of a ...
Text Solution
|
- A sphere of radius 0.1 m and mass 8 pi kg is attached to the lower end...
Text Solution
|
- A sphere of radius 0.1 m and mass 8 pi kg is attached to the lower end...
Text Solution
|
- A steel wire of length 5 m and diameter 10^(-3) m is hanged vertically...
Text Solution
|