A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NTA MOCK TESTS-EQUILIBRIUM TEST (CHEMICAL)-1-SINGLE CHOICE
- Bromine monochloride ( BrCl ) decomposes into bromine and chlorine acc...
Text Solution
|
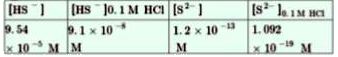
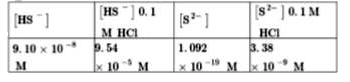
- The first ionization constant of H(2)S is 9.1 xx 10^( -8). Calculate ...
Text Solution
|
- One mole of N(2) (g) is mixed with 2 moles of H(2) (g) in a 4 litre ve...
Text Solution
|
- For the equilibrium, PCl(5) hArr PCl(3) +Cl(2), K(c )=(alpha^(2))/(...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following is correct for the reaction? N(2)(g) +3H(2)(...
Text Solution
|
- In the reaction, H(2)(g) +Cl(2) (g) hArr 2HCl (g):
Text Solution
|
- In which of the following reactions, the concentration of product is h...
Text Solution
|
- The equilibrium constant K(c ) for the reaction P(4) (g) hArr 2P(2)(g)...
Text Solution
|
- The equilibrium constant of the reaction A(2) (g) + B(2) (g) hArr 2AB...
Text Solution
|
- The equilibrium, SO(2)Cl(2)(g) hArr SO(2) (g) + Cl(2) (g) is attained...
Text Solution
|
- The reaction quotient (Q) predicts:
Text Solution
|
- K(p) = 0.04 atm at 899 K for the equilibrium shown below. What is the ...
Text Solution
|
- The equilibrium constant K(c ) for A (g) hArr B (g) is 1.1, gas B will...
Text Solution
|
- X(2) + X^(-) hArr X(3)^(-) (x = iodine) This reaction is set up in aqu...
Text Solution
|
- The partial pressure of CH(3) OH (g), CO((g)) and H(2(g)) in equilibr...
Text Solution
|
- 0.2 mole of NH4Cl are introduced into an empty container of 10 litre a...
Text Solution
|
- For the reaction : CH(4(g)) +2O(2(g)) hArr CO(2(g)) +2H(2)O((l)), W...
Text Solution
|
- In which of the following reactions, increase in the volume at constan...
Text Solution
|
- For the reversible reaction, N(2)(g) +3H(2)(g) hArr 2NH(3)(g) at 50...
Text Solution
|
- At constant temperature, the equilibrium constant (K(p)) for the decom...
Text Solution
|