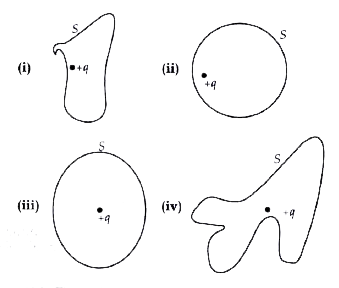A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- The electric flux through the surface :
Text Solution
|
- If the flux of the electric field through a closed surface is zero,
Text Solution
|
- The electric flux through the surface
Text Solution
|
- Electric flux through a spherical surface shown in the figure is
Text Solution
|
- If electric flux passing through a close surface is zero then :-
Text Solution
|
- The electric flux through the surface
Text Solution
|
- A surface enclosed an electric dipole, the flux through the surface is...
Text Solution
|
- The electric displacement current through a surface area "S" is propor...
Text Solution
|
- The Electric flux through the surface:
Text Solution
|