Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
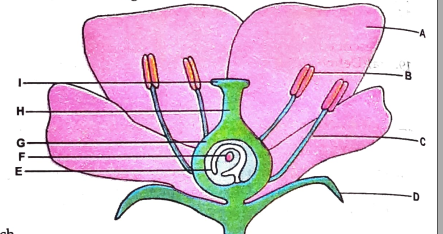
- ADDITIONAL QUESTIONS : The diagram represents a flower. Label the part...
Text Solution
|
- Which type of pollen grains are found in insect pollinated flowers
Text Solution
|
- Pollen grains insect pollinated flowers are
Text Solution
|
- Observe the given diagram and answer the following questions . (iii) W...
Text Solution
|
- The pollen grains of flowers pollinated by insects are:
Text Solution
|
- (a) Identify A, B, and D in the given diagram and write their names. ...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion : Pollination and fertilization in flowers produces fruits a...
Text Solution
|
- (a) Draw a diagram showing germination of pollen on stigma of a flower...
Text Solution
|
- ফুলের কোন্ অংশ ফলে এবং কোন্ অংশ বীজে পরিণত হয় ?
Text Solution
|