Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
MODERN PUBLICATION-AREA OF PARALLELOGRAMS AND TRIANGLES-EXERCISE
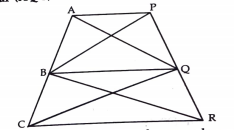
- AP||BQ||CR. Prove that ar(AQC) = ar(PBR)
Text Solution
|
- In the figure. Show that ABCD is a parallelogram. Calculate the are...
Text Solution
|
- Find the area of a rhombus whose diagonals are of lengths 10 cm and 8....
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the area of trap. PQRS, given in the figure.
Text Solution
|
- In the figure. ABCD in a trapezium in which AB||DC. Proe that ar(trian...
Text Solution
|
- In a quad. ABCD it is given that BD = 16 cm. If AL bot BD and CM bot B...
Text Solution
|
- ABCD is a parallelogram whose diagonals intersect at E. AC is produced...
Text Solution
|
- ABCD is a parallelogram whose diagonals intersect at E. AC is produced...
Text Solution
|
- P and Q are respectively the midpoints of sides AB and BC or a triangl...
Text Solution
|
- P and Q are respectively the midpoints of sides AB and BC or a triangl...
Text Solution
|
- P and Q are respectively the midpoints of sides AB and BC or a triangl...
Text Solution
|
- In fig. ABCD and AEFG are two parallelograms. If angleC=55^@ and deter...
Text Solution
|
- ABCD and AEFD are two parallelograms Prove that: ar(triangleAPE) : a...
Text Solution
|
- In Fig. ABCD is a parallelogram. Prove that ar (DeltaACP) = ar (Del...
Text Solution
|
- In triangleABC, it L and M are points on AB and AC respectively such t...
Text Solution
|
- In triangleABC, it L and M are points on AB and AC respectively such t...
Text Solution
|
- D and E are points on sides AB and AC respectively of DeltaABC such th...
Text Solution
|
- D and E are points on sides AB and AC respectively of DeltaABC such th...
Text Solution
|
- ABCD is parallelogram. X and Y are the mid-points of BC and CD respect...
Text Solution
|
- PQRS and PABC are two parallelograms of equal area. Prove that QC||BR
Text Solution
|
- Two parallelograms ABCD and AEFB are drawn on opposite sides of AB. Pr...
Text Solution
|