Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
MODERN PUBLICATION-PROBABILITY-EXERCISE
- Over the apst 200 working days, the number of defective parts produced...
Text Solution
|
- Define a trial.
Text Solution
|
- Define a event.
Text Solution
|
- Define an elementary event.
Text Solution
|
- Define the probability of an event.
Text Solution
|
- When a die is thrown, what are the six possible outcomes?
Text Solution
|
- Describe two events that are sure to happen.
Text Solution
|
- Describe two events that are impossible to happen.
Text Solution
|
- A fair coins is tossed 60 times and it came up with tails 27 times. Fi...
Text Solution
|
- A die is thrown 100 times if the probability of getting an even number...
Text Solution
|
- A coin is tossed 50 times and the tail appears 28 times. In a single t...
Text Solution
|
- True/False: Probability of a sure event is 0.
Text Solution
|
- True/False: Probability of an impossible event is 1.
Text Solution
|
- True/False: If E is an event, then 0 le P(E) le1
Text Solution
|
- True/False: If E is an event, the P(E) + P(notE) = 0
Text Solution
|
- True|false: use the theoretical probability of an event 'E' is 0.47, ...
Text Solution
|
- Can the experiment probability of an event be a negative number? If no...
Text Solution
|
- True/False: The experimental probability of an event cannot be great...
Text Solution
|
- True/False: Out of 35 students participating in a debate 10 are boys...
Text Solution
|
- True/False: The probability of losing a game is 0.7. The probability...
Text Solution
|
- True/False: In a one-day cricket match, a batsman hits the boundary ...
Text Solution
|
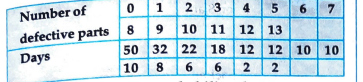 Determine the probability that tommorow's output will have
Determine the probability that tommorow's output will have