Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
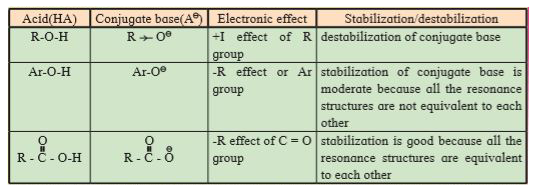
- Alcohols (R-OH), phenols (Ar-OH) and carboxylic acids (R-COOH) can un...
Text Solution
|
- R-COCH(3) overset(X(2)//OH^(-))to CHX(3)+ Carboxylate ion overset(H^(+...
Text Solution
|
- The OH group of an alcohol or the -COOH group of a carboxylic acid can...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion (A) : Al(OH)(3) is amphoteric in nature. Reason (R) : Al-O a...
Text Solution
|
- Explain why phenols do not undergo substitution of the -OH group like ...
Text Solution
|
- Explain why phenol does not undergo substiution of the -OH group like ...
Text Solution
|
- ऐल्कोहॉल के -OH तथा कार्बोक्सिल अम्ल के -COOH समूह -Cl द्वारा निम्नलिख...
Text Solution
|
- Carbolic acid contains functional group Carboxylic - COOH Alcoholic...
Text Solution
|
- The - Oh group of an alcohol or COOH group of a carboxylic acid can be...
Text Solution
|