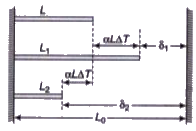
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- What will be the stress at -20^(@)C, if a steel rod with a cross-secti...
Text Solution
|
- There is some change in length when a 33000 N tensile force is applied...
Text Solution
|
- A steel rod of length 5 m is fixed between two support. The coefficien...
Text Solution
|
- A wire of cross sectional area 3mm^(2) is just stretched between two f...
Text Solution
|
- A steel rod with a cross-sectional area of 150 mm^(2) is stretched bet...
Text Solution
|
- A wire of cross-sectional area 3 mm^(2) is first stretched between two...
Text Solution
|
- A rod is fixed between two points at 20^(@)C. The coefficient of linea...
Text Solution
|
- A steel rod (Y = 2.0 xx 10^(11) N//m^(2) " and "alpha = 10^(-50).^(@)C...
Text Solution
|
- A wire of cross sectional area 3 mm^(2) is just stretched between two ...
Text Solution
|