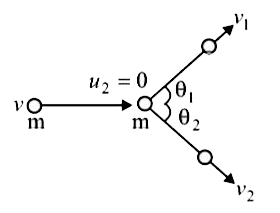
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NTA MOCK TESTS-NTA TPC JEE MAIN TEST 63-PHYSICS
- An aircraft of mass 4 xx 10^(5)kg with total wing area 500m^(2) in lev...
Text Solution
|
- Two blocks each of mass m lie on a smooth table. They are attached to ...
Text Solution
|
- A thin lens is made with as material having refractive index mu=1.5. b...
Text Solution
|
- A rolling body is released from rest on sufficient rough long inclined...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform rod AB of mass m is suspended in equilibrium from two simila...
Text Solution
|
- Three perfect gases at absolute temperature T(1), T(2) and T(3) are mi...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion: The value of specific heat of a gas at constant pressure is...
Text Solution
|
- In Young's double slit experiment, the 10^(th) maximum of wavelength ...
Text Solution
|
- Consider two particles of equal mass m. If one particle is stationary ...
Text Solution
|
- Consider a force vecF = -xhati +yhatj. The particle is moved from poin...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the wavelength of Kbeta line (in Å ) emitted by a hydrogen-...
Text Solution
|
- The photoelectrons are emitted when light of wavelength 150 nm falls o...
Text Solution
|
- For a time-varying electromagnetic wave, the amplitude of the electric...
Text Solution
|
- The above I – V graph shows the characteristics of a p-n junction diod...
Text Solution
|
- Consider a 2 cm thick steel plate with an ultimate shear stress of 3.4...
Text Solution
|
- A soap bubble has surface tension 'T' and its radius 'p'. The mean squ...
Text Solution
|
- A paramagnetic sample shows a net magnetisation of 6 A m^(-1), when pl...
Text Solution
|
- An experiment for determination of velocity of sound by resonance tube...
Text Solution
|
- Heat is produced due to viscous forces when a small sphere of radius r...
Text Solution
|
- Heat is generated uniformly per unit volume inside a spherical volume ...
Text Solution
|