A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
MODERN PUBLICATION-PROBABILITY-EXERCISE
- Let A and B be two events. If P(A)=0.6, P(B)=0.2, P(A/B)=0.5, then P(A...
Text Solution
|
- If A and B are independent events such that 0 lt P (A) lt 1 and 0 lt P...
Text Solution
|
- Let 'X' be a discrete random variable. The probability distribution of...
Text Solution
|
- Let 'X' be a discrete random variable assuming values x1, x2, ...........
Text Solution
|
- Two events A and B will be independent, if:
Text Solution
|
- If A and B are two events such that AcapBnephi, P((A)/(B))=P((B)/(A))...
Text Solution
|
- If P(E)=11/36, P(F)=5/36 and P(EnnF)=2/36, then the value of P(E/F) is...
Text Solution
|
- Two cards are drawn at random and without replacement from a pack of 5...
Text Solution
|
- An urn contains 10 black and 5 white balls. Two balls are drawn from t...
Text Solution
|
- Probability distribution of X is given below, then the value of K is ...
Text Solution
|
- If A and B are any two events such that : P(A) + P(B) – P(A and B) = P...
Text Solution
|
- In a single throw of a pair od die, the probability of getting total o...
Text Solution
|
- A and B are two mutually exclusive events of an experiment. If P (not ...
Text Solution
|
- P(E/F) is equal to :
Text Solution
|
- If P(A)=0.3, P(B)=0.4, find P(AuuB). where A and B are independent eve...
Text Solution
|
- A pair of coins is tossed once. Find the probability of showing at lea...
Text Solution
|
- A and B are events such that 2P(A)=P(B)=5/13, P(A/B)=2/5, then P(AuuB)...
Text Solution
|
- The probability of obtaining an even prime number on each die, when a ...
Text Solution
|
- If P(A)=3/5 and P(B)=1/5, find P(AnnB) if A and B are independent even...
Text Solution
|
- If P(A)=7/13, P(B)=9/13 and P(AnnB)=4/13, evaluate P(A/B).
Text Solution
|
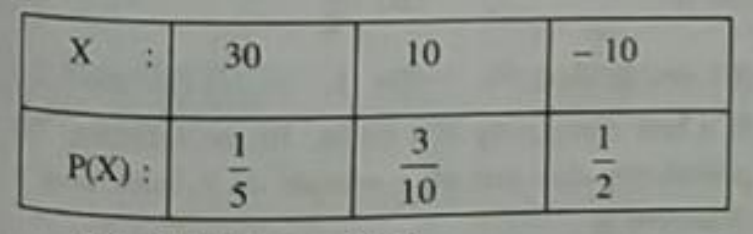 Then E(X) is equal to :
Then E(X) is equal to :