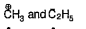A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- Heterolysis of CH3CH2CH3 results in the formation of
Text Solution
|
- Heterolysis of bonds to carbon does not lead to the formation of
Text Solution
|
- Heterolysis of carbon-chlorine bond produces
Text Solution
|
- Heterolysis of propane gives:
Text Solution
|
- Heterolysis of a carbon-chlorine bond produces
Text Solution
|
- The reagent used for the conversion CH3CH2COOH to CH3CH2CH3 , is
Text Solution
|
- Heterolysis of C-Br bond produces
Text Solution
|
- Heterolysis of carbon-chlorine bond produces .
Text Solution
|
- Homolysis of propane gives:
Text Solution
|