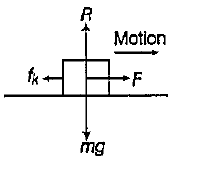
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A hockey puck is given an initial speed of 20 m/s on a frozen pond and...
Text Solution
|
- An air puck of mass m(1) is tied to a string allowed to revolved in a ...
Text Solution
|
- A small puck is sliding to the right with momentum vec(P)(1) on a hori...
Text Solution
|
- A puck of mass m is moving in a circle at constant speed on a friction...
Text Solution
|
- Two pucks are initially moving along a frictionless surface as shown i...
Text Solution
|
- A small puck of mass m asn velcity v slider along a horizonal plane. T...
Text Solution
|
- निम्न में से किस एंजाइम में ताँबा पक सक्रियक के रूप में जुड़ा रहता है-
Text Solution
|
- A stone of 1 kg its thrown with a velocity of 20 m s^(-1) acroos the f...
Text Solution
|
- A stone of 1 kg is thrown with a velocity of 20 m s-1 across the froze...
Text Solution
|