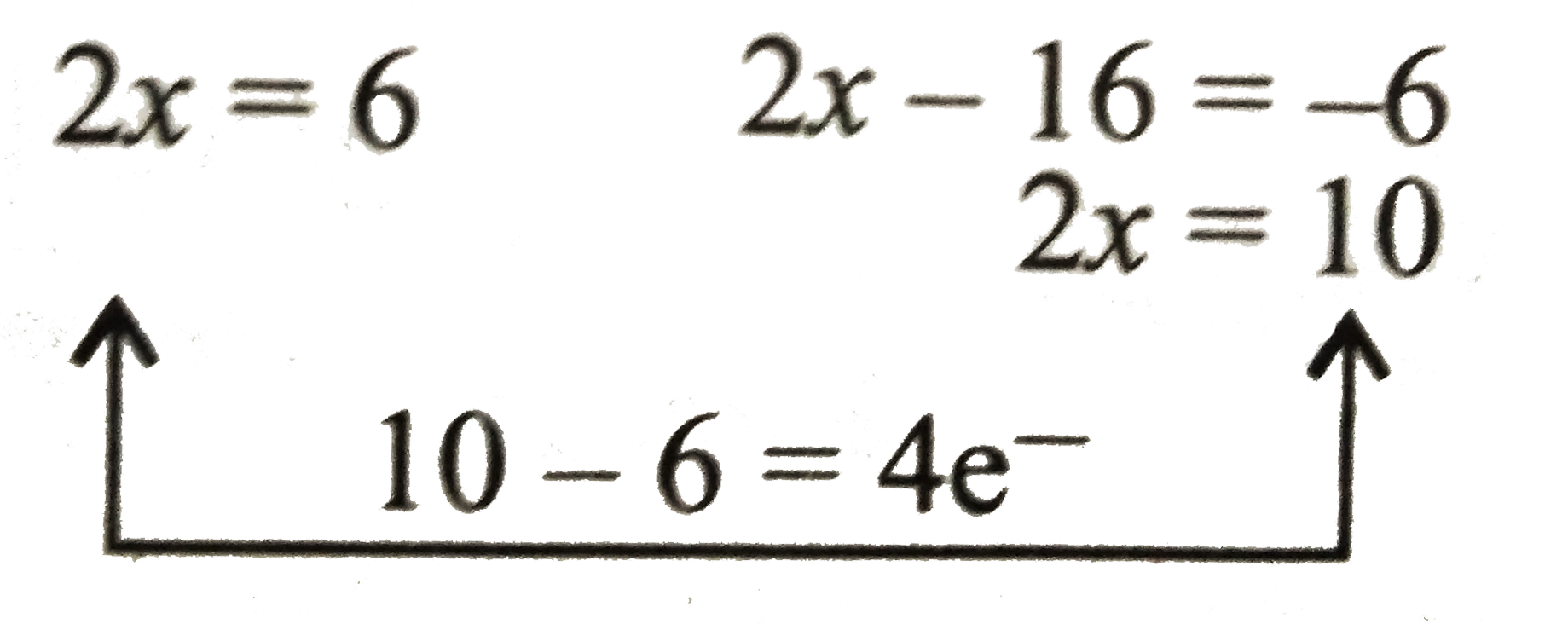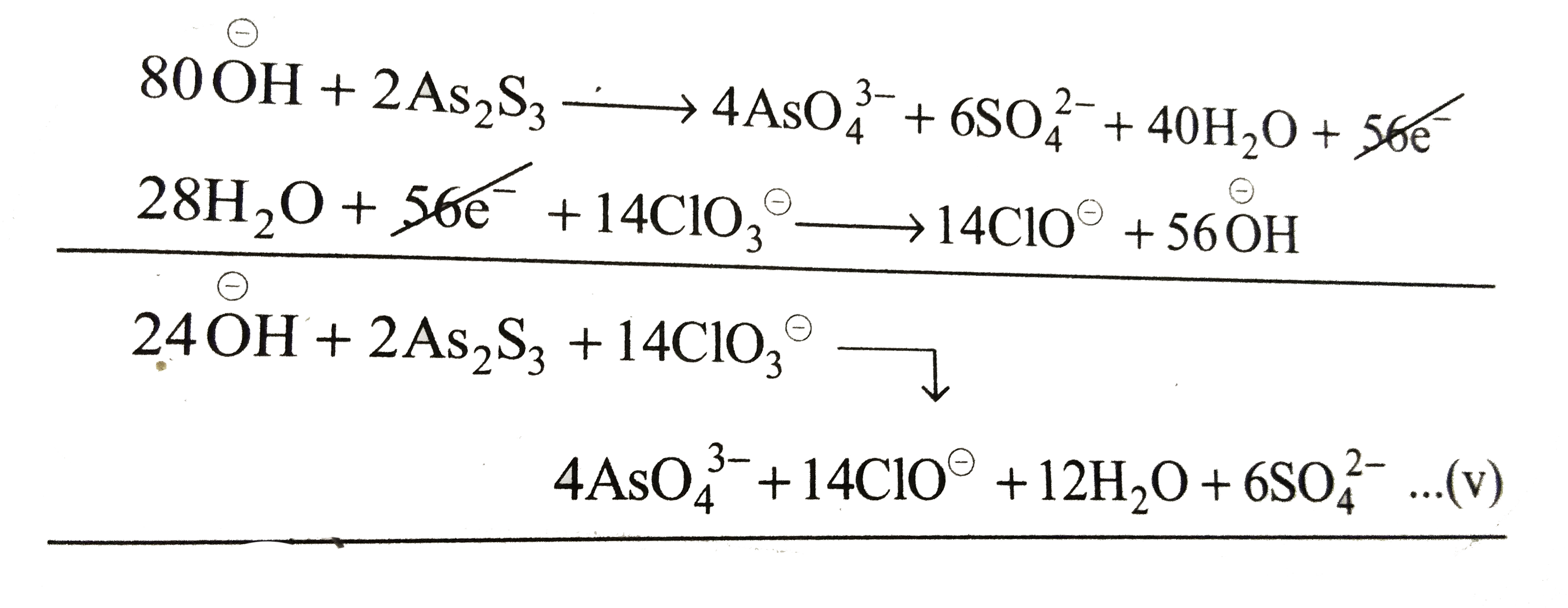`As_(2)S_(3)` is split into two parts `(overset(+3xx2-2xx3)(As_(2)S_(3)))` in which `As_(2)^(6+)` is oxidised to `AsO_(4)^(3-)` and `S_(3)^(6-)` is oxidised to `SO_(4)^(2-)`. Whereas, `ClO_(3)^(ө)` (hypochlorite ion).
b. Write the eqaution in ionic form.
`As_(2)S_(3)+ClO_(3)^(ө)+overset(ө)OHrarrAsO_(4)^(3-)+ClO^(ө)+SO_(4)^(2-)`
c.
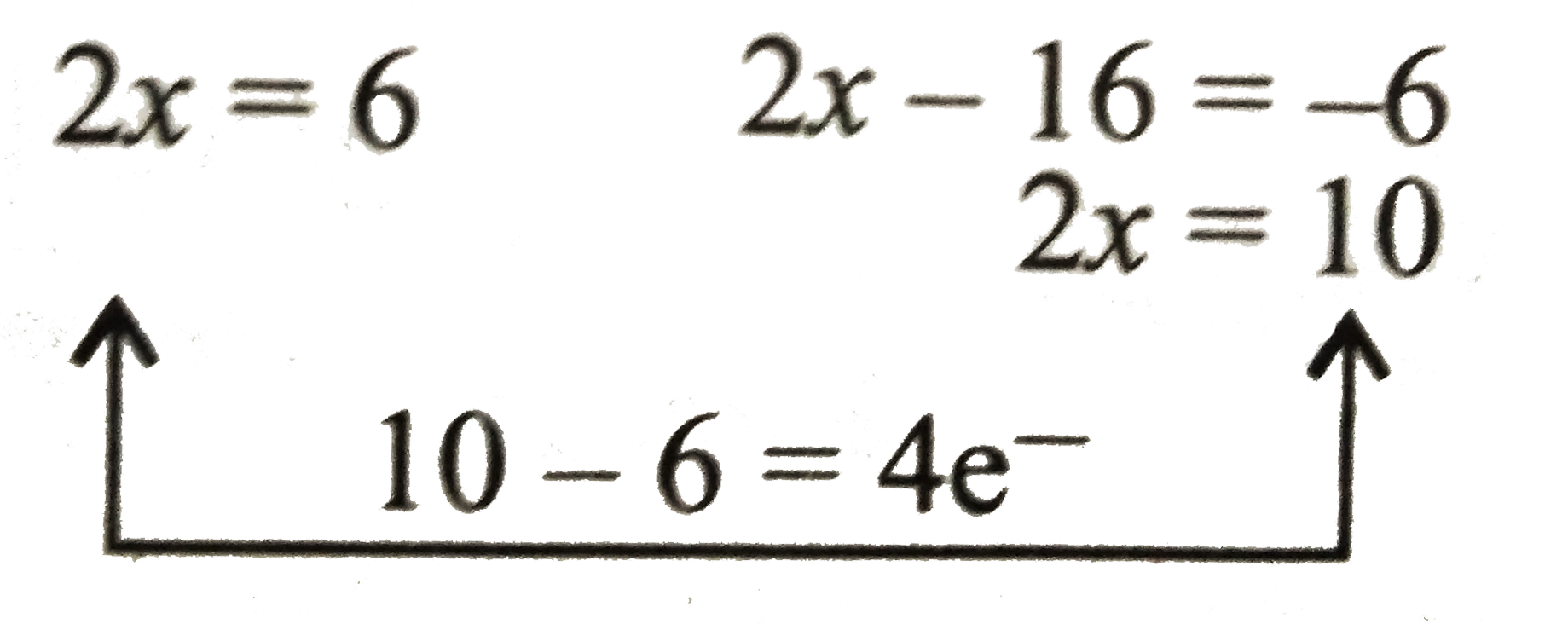
d. Balance `O` atoms by adding `8H_(2)O` on `LHS`
`8H_(2)O+As_(2)^(6+)rarr2AsO_(4)^(3-)+4e^(-)`
e. Balance `H` atoms in basic medium by adding `16H_(2)O` on `RHS` and simultaneously add `16overset(ө)OH` ions to `LHS`.
`16overset(ө)OH+8H_(2)O+As_(2)^(6+)rarrAsO_(4)^(3-)+4e^(-)+16H_(2)O`
or
`16overset(ө)OH+As_(2)^(6+)rarr2AsO_(4)^(3-)+4e^(-)+8H_(2)O`...(i)
It is a balanced equation.
f. Similarly, balance `S_(3)^(6-) t o SO_(4)^(2-)` ion in basic medium

g. Balance `O` atom by adding `12H_(2)O on LHS`.
`12H_(2)O+S_(3)^(6-)rarr3SO_(4)^(2-)+24e^(-)`
h. Balance `H` atom in basic medium by adding `24H_(2)O`on `RHS` and simultaneously add `24oveset(ө)OH` ions on `LHS`.
`24overset(ө)OH+12H_(2)O+S_(3)^(6-)rarr3SO_(4)^(2-)+24e^(-)+24H_(2)O`
or
`24overset(ө)OH+S_(3)^(6-)rarr3SO_(4)^(2-)+12H_(2)O`....(ii)
It is a balanced equation.
i. Now add equations (i) and (ii) to get final oxidation reaction.
`{:(16overset(ө)OH+As_(2)^(6+)rarr2AsO_(4)^(3-)+4e^(-)+8H_(2)O),(24overset(ө)OH+S_(3)^(6-)rarr3SO_(4)^(2-)+24e^(-)+12H_(2)O),(ulbar(40overset(ө)OH+As_(2)S_(3)rarr2AsO_(4)^(3-)+3SO_(4)^(2-)+20H_(2)O+28e^(-))):}` (ii)
j. Similarly, balance the reduction equation of `ClO_(3)^(ө)` to `ClO^(ө)` ion.
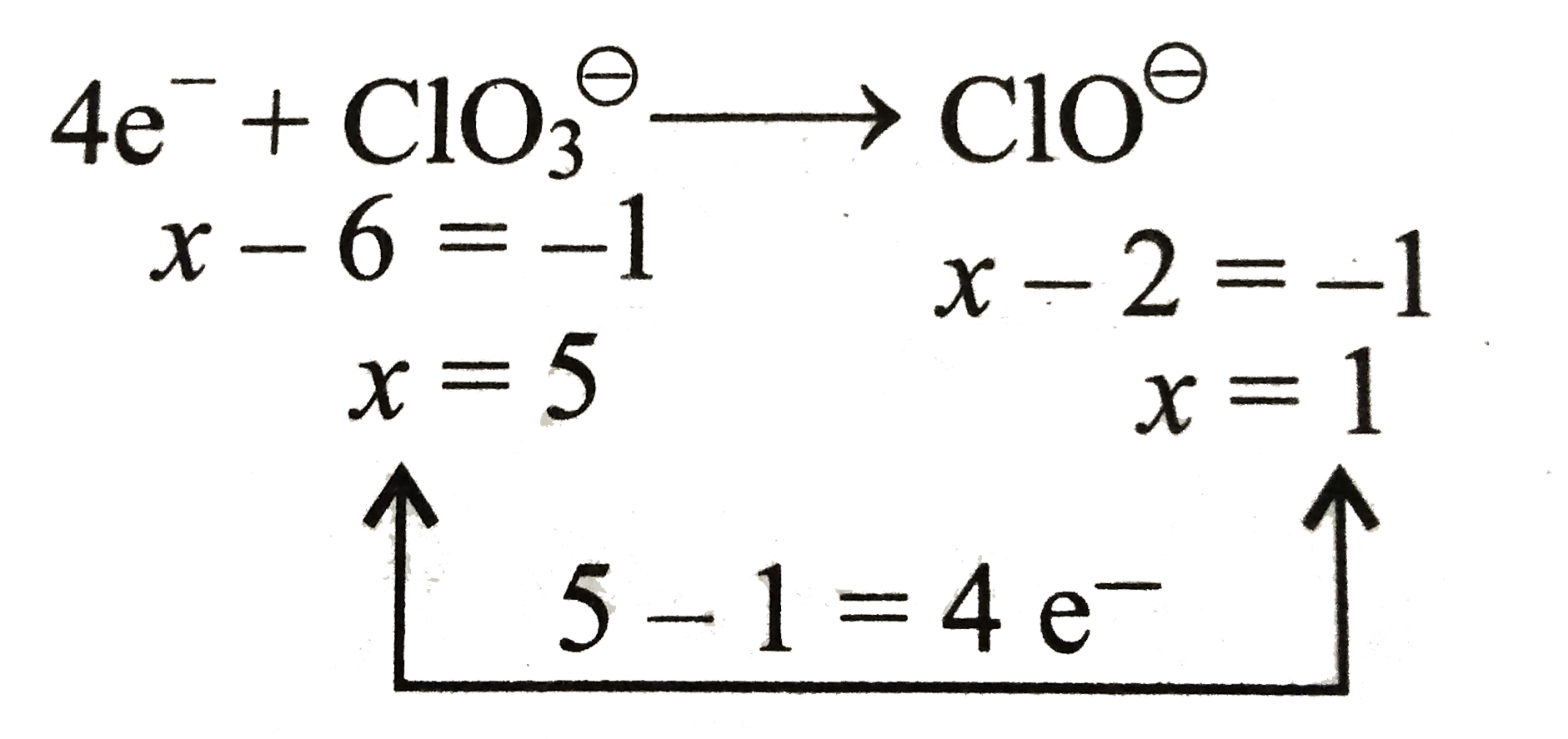
k. Balance `O` atom by adding `2H_(2)O` on `RHS`
`4e^(-)+ClO_(3)^(ө)rarrClO^(ө)+2H_(2)O`
I. Balance `H` atoms in basic medium by adding `4H_(2)O` on `LHS` and simultaneously add `4overset(ө)OH` ions on `RHS`.
`4H_(2)O+4e^(-)+ClO_(3)^(ө)rarrClO^(ө)+2H_(2)O+4overset(ө)OH`
or `2H_(2)O+4e^(-)+ClO_(3)^(ө)rarrClO^(ө)+4overset(ө)OH`.....(iv)
It is a balanced reduction equation.
Equation (iii) is an oxidation reaction and equation (iv) is a reduction equation. To balance the number of electrons, multiply equation (iii) by `2` and equation (iv) by `14` and add them.
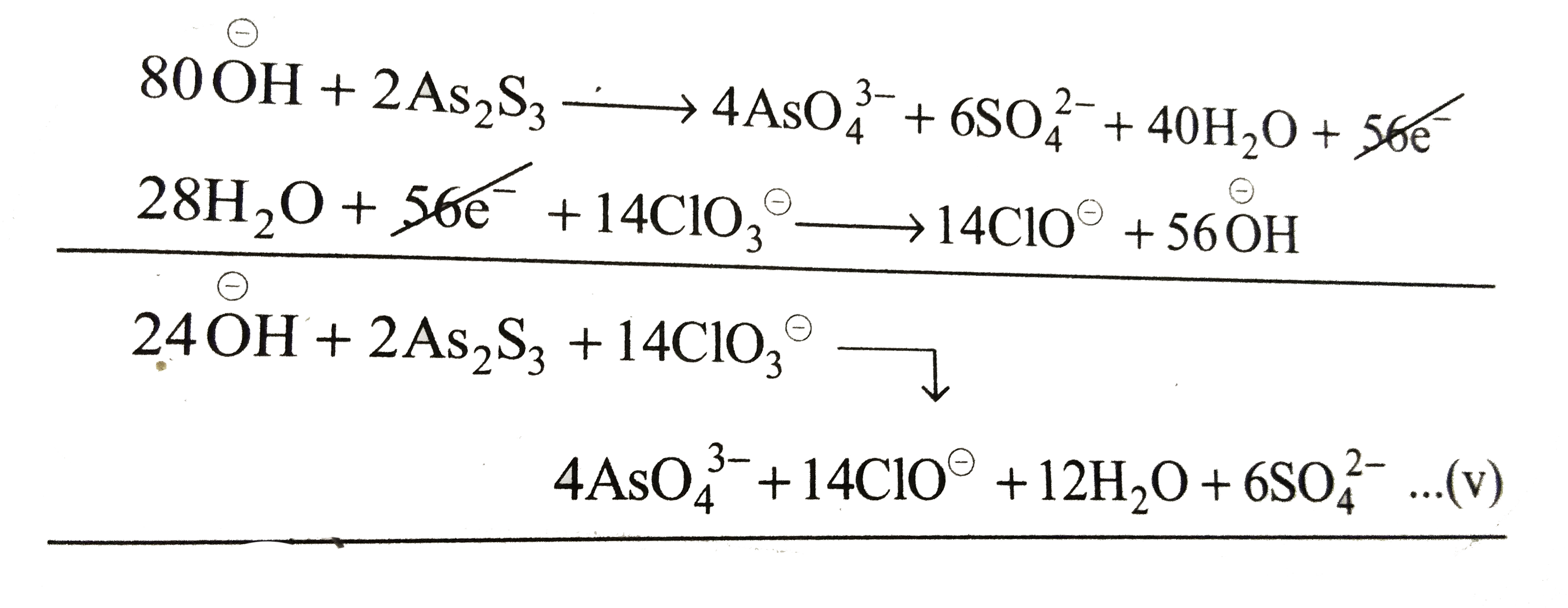
It is a balanced redox reaction.
Now add other ions to both sides of a equation (v).
`LHS[[24Na^(o+)],[14Na^(o+)]]RHS[[24Na^(o+)],[14Na^(o+)]]`
Equation (v) becomes
`24NaOH+2As_(2)S_(3)+14NaClO_(3)rarr4Na_(3)AsO_(4)+14NaClO+6Na_(2)SO_(4)+12H_(2)O`
or
`12NaOH+As_(2)S_(3)+7NaClO_(3)rarr2Na_(3)AsO_(4)+7NaClO+3Na_(2)SO_(4)+6H_(2)O`....(vi)
Equation (vi) is the final balanced redox reaction.
ii. b. The number of electrons involved in equation (iii) is `28`. So the equivalent weight of `As_(2)S_(3) is M//28`.
Answer is (iv).