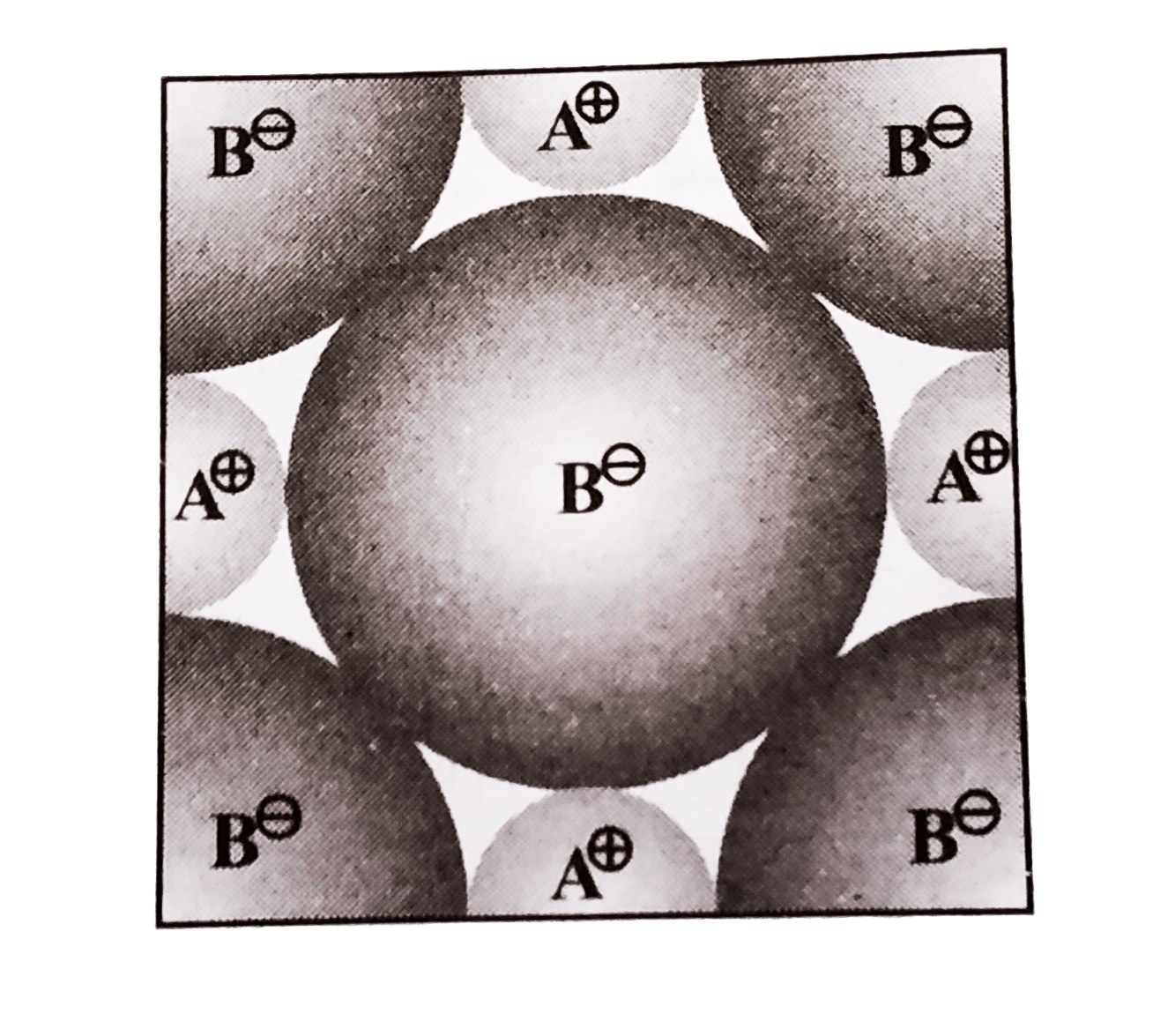
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- If all the atoms touching one face plane are removed in solid A^(o+)B^...
Text Solution
|
- If all the atoms touching one face plane are removed in solid A^(o+)B^...
Text Solution
|
- Name the ionic solid which shows both Schottky defect and Frenkel defe...
Text Solution
|
- Give example for Schottky defect and Frenkel defect ionic solids?
Text Solution
|
- Frenkel and Schottky defects are:
Text Solution
|
- Explain the following terms : (a) Schottky defect (b) Frenkel defect.
Text Solution
|
- Explain Schottky and Frenkel defects.
Text Solution
|
- Explain Schottky and Frenkel defects.
Text Solution
|
- Explain Schottky defect.
Text Solution
|